Wie sollten Lithiumbatterien gelagert werden??
Egal, ob Sie Ersatz -Lithiumbatterien für Ihre Hobbys haben oder ein großes Energiespeichersystem für Ihr Zuhause planen, Es ist entscheidend, zu wissen, wie man sie richtig speichert. Bei der richtigen Lagerung geht es nicht nur um Bequemlichkeit; Es ist wichtig, die Lebensdauer der Batterie zu maximieren und die Sicherheit zu gewährleisten. Also, Was sind die Regeln für die Speicherung dieser fortschrittlichen Technologie??
Für langfristige Lagerung, Lithiumbatterien sollten kühl gehalten werden, Trockener Ort, weg von direktem Sonnenlicht und brennbaren Materialien, in einem teilweisen Verantwortungszustand - idealerweise dazwischen 40% Und 60%. Sie sollten niemals über lange Zeiträume voll aufgeladen oder vollständig erschöpft werden. Für Systeme mit mehreren Modulen, Die Verwendung eines ordnungsgemäßen Lithium -Batterie -Racks oder -schrank, Organisation, und ordnungsgemäße Belüftung.

Bei Gycx Solar, Ein wesentlicher Bestandteil unseres Systemdesigns besteht darin, sicher, und optimale Umgebung. Die richtige Lagerung ist ein Eckpfeiler eines langlebigen und zuverlässigen Energiesystems. Erforschen wir einige der häufigsten Fragen zu diesem Thema.
Was ist das größte Problem mit Lithiumbatterien?
Lithium-Ionen-Batterien sind revolutionär, Aber keine Technologie ist ohne Herausforderungen. Das Verständnis der größten Probleme hilft Ihnen dabei, die Engineering zu schätzen, die in hochwertige Batteriesysteme einfließt und warum die ordnungsgemäße Handhabung und Speicherung so wichtig sind.
Die größten Herausforderungen für Lithiumbatterien sind ihre Vorabkosten, ihre endliche Lebensdauer aufgrund von Verschlechterung, Sicherheitsbedenken Wenn sie beschädigt oder schlecht verwaltet werden (wie das Risiko eines thermischen Ausreißers), Die Umwelt- und ethische Fragen im Zusammenhang mit dem Bergbau Einige ihrer Rohstoffe, und das sich entwickelnde Bereich von Recycling am Lebensende. Modern LFP1. (Lithium -Eisenphosphat) Batteriesysteme, Jedoch, sind so konstruiert, dass viele dieser Schlüsselprobleme spezifisch gemindert werden, insbesondere in Bezug auf Sicherheit und materielle Beschaffung.
Tauchen tiefer: Eine ausgewogene Sicht auf die Herausforderungen der Lithiumbatterie
Schauen wir uns diese Probleme ausführlicher an:
- Kosten: Hochwertige Lithiumbatterien sind eine erhebliche Investition. Die komplexe Fertigung und die Rohstoffkosten tragen dazu bei.
- Unsere Perspektive: Wir ermutigen, die Kosten über das gesamte Leben der Batterie zu betrachten. LFP -Batterien bieten Tausende mehr Zyklen als ältere Technologien, Oft die wirtschaftlichere Wahl machen 10-15 Jahre.
- Verschlechterung: Alle Batterien verlieren mit Alter und Gebrauch die Kapazität.
- Unsere Perspektive: Dies ist ein überschaubarer Faktor. Durch Auswahl einer dauerhaften Chemie wie LFP, Sicherstellen, dass die richtige Ladevorgänge gewährleisten, und die Batterie richtig aufbewahren (Kühle Temperaturen, Teilgebühr), Sie können seine Lebensdauer maximieren und Jahre bekommen, oft Jahrzehnte, von zuverlässigem Service.
- Sicherheit (Thermalausreißer): Das Risiko des Feuers, obwohl statistisch niedrig mit Qualitätsprodukten, ist ein ernstes Problem. Es kann durch interne Mängel verursacht werden, physischer Schaden, oder schweres Überladen.
- Unsere Perspektive: Hier ist die LFP-Chemie ein Game-Changer. Es ist weitaus chemisch stabiler und weniger anfällig für thermische Ausreißer als andere Lithium-Ionen-Typen. Das, kombiniert mit einem ausgeklügelten Batteriemanagementsystem (BMS) und professionelle Installation, macht moderne LFP -Energiespeichersysteme außergewöhnlich sicher.
- Rohstoffbeschaffung: Der Bergbau von Materialien wie Lithium und insbesondere Kobalt hat umweltbezogene und ethische Fragen aufgeworfen.
- Unsere Perspektive: Dies ist ein weiterer Grund, warum wir die LFP -Technologie bevorzugen, wie es enthält keinen Kobalt, ein wichtiger Anlass zur Sorge. Dies macht es zu einer stabileren und ethisch fundierten Wahl.
- Recycling: Während die Lithiumbatterie -Recyclingindustrie schnell wächst, Es reift immer noch.
- Unsere Perspektive: Wir unterstützen und ermutigen das verantwortungsvolle Management am Lebensende. Wenn immer mehr Batterien in den Markt eintreten, Recyclinginfrastruktur und -prozesse erweitern sich, um eine kreisförmigere und nachhaltigere Batteriewirtschaft zu schaffen.
Entladen sich Lithiumbatterien, wenn sie nicht benutzt werden??
Sie haben Ihre Batterie richtig gespeichert, Aber Sie könnten sich Sorgen machen, dass es leer wird, wenn Sie es endlich brauchen. Verlieren Lithiumbatterien ihre Ladung, nur in einem Regal zu sitzen??
Ja, alle Batterien, einschließlich Lithium-Ionen, wird langsam abfließen, wenn er aufgrund eines natürlichen Prozesss, der als "Selbstentladung" nicht verwendet wird, nicht verwendet wird." Jedoch, Einer der großen Vorteile moderner Lithium-Ionen-Batterien ist, dass ihre Selbstentladungsrate ist extrem niedrig, normalerweise nur um 1-3% pro Monat. Dies ist deutlich besser als ältere wiederaufladbare Batterie-Technologien wie NIMH oder Lead-Sacid, Dies kann einen erheblichen Prozentsatz ihrer Ladung viel schneller verlieren.
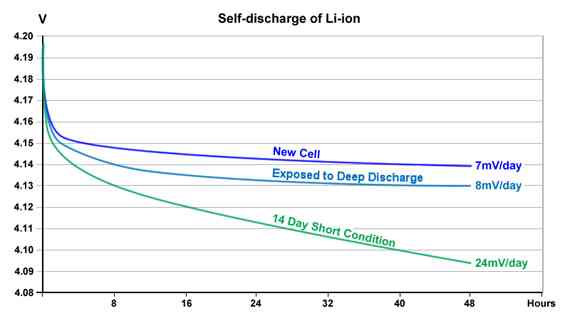
Tauchen tiefer: Das langsame Leck von Selbstentladung
Folgendes sollten Sie über diesen langsamen Abfluss wissen:
- Was verursacht es?: Selbstentladung wird durch sehr langsame interne chemische Reaktionen verursacht, die auch dann auftreten, wenn die Batterie mit nichts verbunden ist. Es ist eine inhärente Eigenschaft der Chemie einer Batterie.
- Warum Lithium besser ist: Die Chemie von Lithium-Ionen-Batterien ist im Leerlauf einfach stabiler im Vergleich zu älteren Typen. Eine versiegelte Blei-Säure-Batterie könnte verlieren 5% seiner Gebühr im ersten Monat, Während eine Qualitäts -LFP -Batterie weniger verliert als 2%.
- Rolle der Temperatur: Die Selbstentladungsrate wird durch die Temperatur beeinflusst. Speichern einer Batterie in einer heißen Umgebung (Wie ein nicht im Luft konditionierter Raum in Singapur) wird seine Selbstentladungsrate erhöhen. Das Speichern an einem kühlen Ort verlangsamt es noch weiter.
- Praktische Implikationen: Für kurz- bis mittelschwere Lagerspeicherung (ein paar Monate), Die von einer Lithiumbatterie verlorene Ladungsmenge ist fast vernachlässigbar. Für sehr langfristige Speicherung (über ein Jahr), Es ist eine gute Idee, das Ladungsniveau der Akku regelmäßig zu überprüfen und das Ideal zu übertreffen 40-60% Speicherebene bei Bedarf.
- Standby Drain vs. Selbstentladung: Verwechseln Sie die Selbstentscheidung nicht mit dem Standby-Abfluss eines Geräts. Wenn eine Batterie in einem Gerät zurückbleibt, das "aus ist" aber immer noch eine kleine Menge an Kraft ziehen (Wie für eine Uhr oder einen Fernsensor), Es wird viel schneller abfließen als eine Batterie, die vollständig getrennt oder separat gespeichert ist.
Ist es am besten, Lithiumbatterien aufgeladen oder ungeladen zu lassen??
Dies ist eine kritische Frage für die langfristige Speicherung. Um die Lebensdauer Ihrer Batterie zu maximieren, Was ist der ideale Gebührszustand, um ihn zu lassen, wenn Sie ihn für einen längeren Zeitraum nicht verwenden?? Sollte es sein 100% voll und bereit zu gehen, oder völlig leer?
Für langfristige Lagerung, Es ist am besten, Lithiumbatterien bei a zu lassen Teilnahmeberechnung, idealerweise dazwischen 40% Und 60%. Speichern einer Lithiumbatterie in vollem Umfang 100% aufladen oder völlig leer werden 0% Viele Monate können zu einem beschleunigten Abbau führen und die Kapazität und die Lebensdauer dauerhaft verringern. Der "Mittelweg" ist der gesündeste Ort für eine müßige Batterie.
Tauchen tiefer: Die Wissenschaft des Speicherzustands
Warum ist die mittlere Reichweite am besten für die Aufbewahrung??
- Das Problem mit 100% (Hochspannungsspannung): Wenn eine Lithium-Ionen-Batterie aufgeladen wird 100%, Die innere Spannung befindet sich auf ihrem Höhepunkt. Durch die Aufrechterhaltung dieser hohen Spannung für längere Zeiträume wird die Komponenten der Batterie belastet, insbesondere die Kathode. Dies beschleunigt einen Prozess namens "Kalenderalterung"," was zu einem schnelleren dauerhaften Kapazitätsverlust führt. Während robuste Chemien wie LFP dies besser umgehen als andere, Das Prinzip bleibt: Eine niedrigere Spannung entspricht weniger Spannung während der Lagerung.
- Das Problem mit 0% (Tiefentladungsrisiko): Es ist ebenfalls gefährlich, eine Batterie in einem sehr geringen Ladungszustand zu speichern. Aufgrund der natürlichen Selbstentladung, Die Spannung der Batterie sinkt weiterhin langsam. Wenn es unter eine bestimmte kritische Niederspannungsschwelle fällt, Es kann irreversible chemische Reaktionen auslösen, wie die Auflösung von Kupfersammlern in der Zelle, Dies kann dauerhafte Schäden verursachen und die Batterie nicht sicher aufgeladen werden. Das interne BMS der Batterie wird ebenfalls heruntergefahren und kann möglicherweise nicht aufwachen" Wenn die Spannung zu niedrig fällt.
- Der 40-60% "Glücklicher Ort": Aufbewahrung bei einer Teilgebühr von rund um 40-60% Steckt die Batterie in eine Stress mit geringem Stress, stabiler Spannungszustand. Es ist hoch genug, um zu verhindern, dass eine tiefe Entladung über viele Monate selbst entlastet, aber niedrig genug, um den Kalenderalterungsprozess, der bei voller Ladung auftritt, erheblich zu verlangsamen.
Praktische Schritte für die Lagerung: Wenn Sie eine Lithiumbatterie aufbewahren müssen (oder ein Gerät, das von einem betrieben wird):
- Laden oder entladen es, bis es ungefähr erreicht 50%.
- Wenn möglich, Schalten Sie das Gerät vollständig aus oder trennen Sie den Akku.
- Lagern Sie es in einem coolen, Trockener Ort.
- Für sehr lange Speicherung (Z.B., mehr als 6-12 Monate), Überprüfen Sie das Ladungslevel regelmäßig und übertreffen Sie es wieder auf 50% bei Bedarf.
Wo nicht Lithium -Batterien aufbewahrt werden?
Sie kennen den idealen Gebührenzustand für die Lagerung, Aber der physische Ort ist für Sicherheit und Langlebigkeit genauso wichtig. Was sind die Umgebungen und Orte, die Sie bei der Speicherung Ihrer Lithiumbatterien unbedingt vermeiden sollten??
Du solltest Lagern Sie niemals Lithiumbatterien an Orten mit extremen Temperaturen, wie ein heißer Dachboden, im direkten Sonnenlicht, oder eine eisige Garage im Winter. Vermeiden feuchte oder feuchte Orte wo Feuchtigkeit Korrosion verursachen kann. Und für Brandschutz, Lagern Sie sie nicht in der Nähe von brennbaren Flüssigkeiten oder anderen brennbaren Materialien. Im Wesentlichen, eine coole, trocken, stabil, und sicherer Ort ist das, was Sie brauchen, und für systemisierte Batterien, ein richtiges Lithium-Batterie-Rack ist die ideale Lösung.

Tauchen tiefer: Auswahl einer sicheren Speicherumgebung
Hier ist eine Checkliste von Orten und Bedingungen, die Sie vermeiden sollten:
- Extreme Hitze: Dies ist der kritischste Faktor, Besonders in einem tropischen Klima wie von Singapur. Lagern Sie niemals Batterien in einem Autokoffer, Ein Metallschuppen in der Sonne, Ein nicht iinsulierter Dachboden, oder an einem Ort, der sehr heiß wird. Wärme ist der Killer Nummer eins der Akkulaufzeit.
- Extrem kalt: Lagern Sie keine Batterien an Orten, an denen sie einfrieren konnten (unter 0 ° C oder 32 ° F). Während die Lagerung in der Kälte weniger schädlich ist als Hitze, Versuch zu Aufladung Eine gefrorene Batterie kann dauerhafte Schäden verursachen.
- Hohe Luftfeuchtigkeit / Nasse Bereiche: Vermeiden Sie feuchte Keller, undichtes Schuppen, oder jeder Bereich, in dem die Batterie Feuchtigkeit ausgesetzt sein könnte. Wasser kann Klemmen korrodieren und die elektronischen Komponenten des BMS beschädigen.
- In der Nähe von entzündbaren Materialien: Während hochwertige LFP -Batterien sehr sicher sind, Es ist eine grundlegende Sicherheitsvorsorge, neben Benzin niemals ein energiegeladenes Gerät zu speichern, Propantanks, Lösungsmittel, oder Stapel brennbarer Materialien wie fettige Lumpen.
- Instabile oder hohe Verkehrsbereiche: Speichern Sie keine Batterien, wo sie leicht umgeschlagen werden könnten, gestoßen, durchpacht, oder zerquetscht.
- Die ideale Speicherlösung: Ein richtiger Batterie -Rack
GYCX Solar Story: "Wenn wir ein Solarspeichersystem entwerfen, Ein großer Teil unseres Jobs besteht darin, den besten Ort zu finden. Für einen Kunden mit mehreren Batteriemodulen, Wir haben eine professionelle Qualität installiert, Schloss Lithium -Batterie -Rack in ihrem Versorgungsraum. Dies hält die Batterien sicher, sorgt für den richtigen Abstand für die Belüftung, schützt sie vor körperlichem Schaden, und führt zu sauber, sichere Installation. Es ist der professionelle Standard für die Speicherung eines Multi-Modul-Systems."
Ein dediziertes Gestell oder Schrank bietet die perfekte Coole, trocken, sicher, und organisiertes Zuhause für Ihr wertvolles Batteriesystem.
Das ordnungsgemäße Speichern Ihrer Lithiumbatterien ist einfach, wenn Sie ein paar goldenen Regeln befolgen: Halten Sie sie bei einer Teilbeschuldigung (40-60%) in einer kühlen, trocken, und sicherer Standort. Durch das Verständnis und Vermeiden der wichtigsten Nachteile und Stressoren, Sie können die Lebensdauer Ihrer Investition erheblich verlängern. Für Multi-Modul-Systeme, Verwenden eines speziell gebauten Lithium-Batterie-Rack ist die beste Verfahren, um Sicherheit und Organisation zu gewährleisten.
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen zum Entwerfen einer sicheren und lang anhaltenden Energiespeicherlösung haben, Das Expertenteam von GYCX Solar ist hier, um zu helfen. Kontaktieren Sie uns für eine professionelle Beratung!
Wenn Sie das Konzept von LFP verstehen. Auf diese Weise können Sie das Produkt auswählen, das Ihren Anforderungen von unserem Unternehmen am besten entspricht. ↩
