Puede poner la batería de litio en agua.?
En general, La combinación de agua y electricidad conlleva riesgos..
¿Qué significa colocar baterías de litio en agua para el uso de la batería??
Esta pregunta trata sobre las posibles reacciones que pueden ocurrir cuando las baterías de litio entran en contacto con el agua., destacando la importancia de la seguridad de la batería en el uso.
Esta guía proporcionará una comprensión integral de los riesgos potenciales y las estrategias de prevención..
Dominar estas interacciones es crucial para garantizar la seguridad de la batería.
Composición química de baterías de litio: componentes centrales.
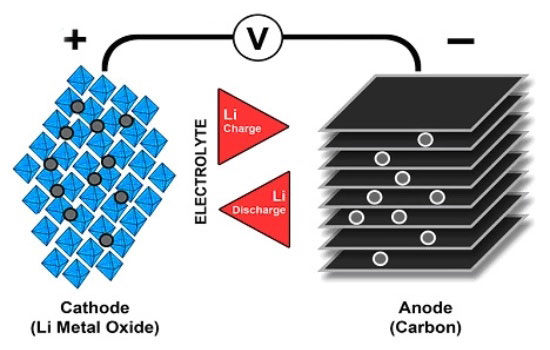
La eficiencia de las baterías de litio proviene de la colaboración precisa de componentes internos clave., incluido:
Polos positivo y negativo de la batería.
Electrodo positivo (cátodo):
Compuesto por materiales como óxido de litio y cobalto., fosfato de hierro y litio, u óxido de litio y manganeso.
El electrodo positivo sirve como fuente de liberación de iones de litio durante la descarga..
electrodo negativo (ánodo):
Generalmente hecho de materiales de carbono como el grafito..
El electrodo negativo ayuda con la inserción y extracción de iones de litio para mantener el equilibrio de carga de la batería..
Electrolito de batería
El electrolito es un disolvente orgánico que contiene sales de litio..
Como medio para el transporte de iones., Permite que los iones de litio se muevan entre los electrodos positivo y negativo., logrando así la función de carga y descarga de la batería.
Separador de batería
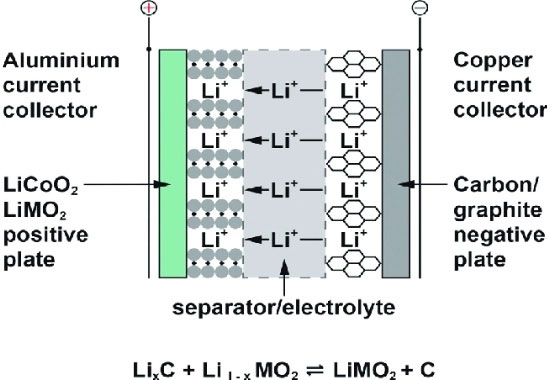
El separador de batería sirve como capa de aislamiento físico entre los electrodos positivo y negativo., evitando el contacto directo entre ambos y provocando un cortocircuito.
Al mismo tiempo, Asegúrese de que los iones de litio puedan pasar sin problemas durante el proceso de carga y descarga..
La interacción entre estos componentes químicos afecta directamente el rendimiento de la batería en diversas condiciones de trabajo..
La reacción química entre la batería de litio y el agua.
La fuerte reactividad entre el litio y el agua significa que la humedad dentro de las baterías de litio puede desencadenar reacciones químicas de alto riesgo..
Después de que el agua se filtre en las baterías de litio, Desencadena una serie de cambios químicos dañinos., incluida la generación de calor, liberando gas hidrógeno, y aumentando el riesgo de incendio.
Impacto directo:
Una vez que las baterías de litio entran en contacto con la humedad, inmediatamente mostrarán signos de mal funcionamiento, como calentar y fumar.
Estos fenómenos inmediatos son el resultado de la rápida reacción entre la humedad y los materiales internos de la batería..
Generación de hidrógeno:
La presencia de humedad puede provocar la descomposición de los compuestos de litio en el interior de la batería., productor hidrógeno gas.
Esta ecuación química es:
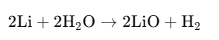
Después de mezclar con aire, este gas puede formar una mezcla explosiva, aumentar el riesgo de incendio o explosión.
Fenómeno de fiebre:
La entrada de humedad en la batería puede provocar una reacción exotérmica, provocando un fuerte aumento de la temperatura.
Este calentamiento rápido puede hacer que la batería se incendie o explote., representando un peligro importante para la seguridad.
Riesgos de incendio y altas temperaturas.:
La combinación de ambientes de alta temperatura., gases inflamables (como el hidrógeno), y los componentes de la batería potencialmente inflamables pueden provocar incendios..
Una vez que se produce un incendio, Estos incendios son difíciles de extinguir y pueden causar importantes daños a la propiedad y amenazar la seguridad del personal..
Debido a la incertidumbre de las propiedades de los materiales y las situaciones involucradas., controlar o extinguir tales incendios se ha vuelto extremadamente desafiante.
Posibles situaciones de contacto con el agua.:
Las baterías de litio pueden entrar en contacto con la humedad en caso de inundaciones, fugas, o almacenamiento inadecuado.
Cada situación trae riesgos específicos, y reconocer estos riesgos ayuda a los usuarios a prevenir peligros potenciales.
Por ejemplo, en los últimos años, Los almacenes que almacenan baterías de litio han sufrido incendios debido a las inundaciones que provocaron que la batería de iones de litio quedara en el agua..
Este incidente resalta los riesgos potenciales asociados con el almacenamiento inadecuado..
¿Qué pasa si se moja una batería de litio??

¿Se pueden mojar las baterías de litio??
La respuesta concisa es que depende de la calidad de la batería y del diseño del fabricante..
La batería de litio GycxSolar tiene una característica completamente sellada., alto nivel de protección, y puede resistir salpicaduras de agua, manteniendo un buen rendimiento incluso en ambientes húmedos.
La cantidad y duración de la intrusión de agua pueden afectar significativamente la vida útil de las baterías..
La mayoría de las baterías de litio tienen cierto grado de sellado., que puede soportar lluvias ligeras o salpicaduras ocasionales de agua, proporcionando protección básica a prueba de agua.
Pero nunca deben sumergirse en agua..
Porque la exposición prolongada a ambientes de alta humedad puede permitir que el vapor de agua se filtre en la batería., causando daños permanentes.
Por lo tanto, aunque la humedad moderada no es un problema para las células GycxSolar, todavía pueden mantener una alta eficiencia.
Pero para todas las baterías de litio., Siempre es necesario evitar el contacto excesivo con la humedad..
Para otros productos de baterías de iones de litio, Es fundamental comprender las especificaciones de impermeabilidad proporcionadas por el fabricante..
Es beneficioso seguir las instrucciones del fabricante y tomar medidas adicionales para evitar el contacto con la humedad..
¿Es peligroso el litio en el agua??
¿Es peligrosa la batería de litio en el agua??
¿Qué sucede cuando las baterías de litio se exponen a ambientes húmedos??
Normalmente, si el grado y la duración de la exposición a la humedad son limitados, no pueden ocurrir problemas.
Las baterías de litio GycxSolar se benefician de su diseño sellado, que puede resistir salpicaduras de agua y proteger los componentes principales de la batería contra daños.
Sin embargo, si la batería está en contacto con el agua durante mucho tiempo, puede causar daño, especialmente a componentes sensibles como terminales de batería.
Una vez que la humedad se filtra en el interior de la batería, puede desencadenar reacciones químicas peligrosas, conduciendo a problemas más graves.
Si una batería de litio está completamente sumergida en agua, La corriente puede conducirse a través del agua entre los terminales..
Esto provocará una descarga anormal de la batería., lo que puede causar daños a la batería.
¿Cuáles son los efectos de la exposición al agua salada en las baterías de litio??
No todos los tipos de agua tienen el mismo impacto en las baterías.
Comparado con el agua dulce, Las baterías expuestas al agua salada pueden sufrir daños más graves y degradación del rendimiento..
La sal disuelta en agua salada puede corroer los componentes y los cables de conexión de las baterías..
Además, La conductividad del agua salada es mayor que la del agua dulce..
Esto significa que cuando el agua salada entra en contacto con los terminales de la batería, puede causar una descarga inesperada de la batería.
¿Puedes cargar una batería de litio húmeda??
Aunque mantener la batería seca es la mejor práctica, Es posible que la carga no se vea afectada si la batería solo encuentra una pequeña cantidad de humedad o se encuentra en un ambiente moderadamente húmedo..
Si la batería está completamente sumergida en agua, no intentes cargarlo.
Si sospecha que la humedad ha dañado la batería de litio, por favor no intentes cargarlo.
En este momento, Se deben tomar medidas de seguridad apropiadas para el manejo..
Medidas impermeables para baterías de litio.
Cómo evitar que las baterías de litio se humedezcan?
Aunque una pequeña cantidad de humedad puede no causar daños a la batería, Tomar algunas medidas preventivas básicas puede minimizar los problemas que la humedad puede causar..
Si no se puede evitar el contacto con la humedad, El uso de cajas o compartimentos de baterías impermeables también puede proporcionar la protección necesaria..
Instale la batería en un lugar protegido e impermeable tanto como sea posible..
Por ejemplo, garajes, trasteros, gabinetes interiores, u otros espacios cerrados son opciones ideales para almacenar baterías.
En condiciones climáticas adversas, como lluvia intensa o cuando se utilizan baterías de litio en barcos o vehículos, Es recomendable evitar al máximo el contacto entre la batería y el agua para mantenerla seca..
Cómo mejorar el rendimiento a prueba de agua de las baterías?
Si espera que las baterías de litio estén expuestas con frecuencia a ambientes húmedos, Se les puede aplicar un tratamiento impermeable adicional..
Para garantizar la sequedad y la seguridad dentro del compartimento de la batería., se pueden utilizar los siguientes métodos:
Envuelva la batería en materiales impermeables como un revestimiento de poliuretano., revestimiento de silicona o caucho.
Mientras los terminales y otros componentes críticos de la batería permanezcan disponibles, Estos materiales pueden proporcionar una capa protectora adicional para las baterías de litio..
Algunos pescadores en hielo utilizan paquetes de baterías especialmente diseñados para mantener las baterías calientes y secas..
Estos contenedores cerrados pueden evitar que las baterías se dañen por la humedad u otros factores durante el transporte..
El tratamiento impermeable es un paso clave para proteger las baterías de posibles daños por humedad., especialmente cuando las baterías pueden estar expuestas a ambientes húmedos.
Existen varias estrategias que pueden proporcionar eficazmente protección impermeable para las baterías., garantizando su rendimiento y seguridad.
Sellado y tratamiento superficial.:
Una forma de proteger los componentes de la batería de los daños causados por la humedad es utilizar materiales impermeables para el embalaje o el tratamiento de recubrimiento..
Por ejemplo, Los recubrimientos a base de silicona o compuestos de encapsulado pueden proporcionar una capa de protección sellada para las baterías., bloqueando eficazmente la humedad.
Esta medida ayuda a mantener la integridad estructural de la batería y garantizar la seguridad de sus componentes internos..
Materiales de embalaje y revestimiento especializados.:
El uso de recubrimientos profesionales, como compuestos para macetas de poliuretano, puede lograr de manera eficiente efectos a prueba de humedad..
En escenarios de aplicaciones de alta gama, escuela politécnica (p-xileno) Los recubrimientos se utilizan ampliamente en equipos industriales y médicos debido a sus características ultrafinas y uniformes..
Construcción de carcasa impermeable:
Los fabricantes de baterías suelen diseñar carcasas de baterías con características impermeables para garantizar la seguridad de los componentes internos..
Estas carcasas suelen estar hechas de materiales resistentes como policarbonato o plástico ABS., que tienen un buen rendimiento de sellado y pueden soportar ambientes húmedos.
En el diseño de la carcasa., También se incorporan componentes como juntas tóricas y juntas tóricas para lograr un sellado más hermético y evitar aún más que entre humedad en la batería..
Agentes selladores y adhesivos.:
Los agentes selladores y adhesivos desempeñan un papel crucial en la prevención de la intrusión de agua..
Aplicar sellador de silicona o epoxi a las costuras., articulaciones, o las aberturas de la carcasa de la batería pueden mejorar la impermeabilización.
Estos selladores pueden sellar eficazmente cualquier posible entrada de agua..
Embalaje protector:
En algunos casos, El uso de protección adicional o envoltura retráctil alrededor de la batería puede proporcionar una capa impermeable adicional..
Por ejemplo, Cinta o envoltura retráctil impermeable diseñada específicamente para proteger la batería..
Todos estos pueden proporcionar una capa protectora impermeable..
Método económico de impermeabilización de bricolaje.:
Para usuarios individuales, Algunas técnicas básicas pueden proporcionar protección efectiva a las baterías en ambientes húmedos.:
Envuelva firmemente la batería pequeña con una bolsa impermeable para asegurar un sellado hermético..
Aplique sellador de silicona en las áreas vulnerables de la carcasa de la batería para evitar la infiltración de humedad..
Antes de usar baterías en aplicaciones críticas, asegúrese de probar su solución impermeable de bricolaje en un ambiente controlado.
Nivel de protección (IP):
Elegir baterías con clasificaciones IP más altas es una estrategia eficaz para lograr la impermeabilización.
El nivel IP especifica detalladamente el nivel de protección contra partículas sólidas e intrusión de agua..
Baterías con clasificaciones IP más altas (como IP67 o IP68) pueden proporcionar una excelente protección contra la humedad y son adecuados para su uso en entornos hostiles.
Sin embargo, Vale la pena señalar que no todas las baterías deben referirse a este valor..
Algunas baterías tienen un IP bajo porque no están diseñadas para uso en exteriores.
Por lo tanto, primero debe comprender el escenario de su aplicación y elegir el nivel de IP apropiado..
En lugar de buscar ciegamente clasificaciones de IP.
Inspección y mantenimiento regulares:
La inspección y el mantenimiento periódicos son cruciales para mantener la eficacia de las medidas de impermeabilización..
Compruebe si hay signos de desgaste, daño, o falla del sello y repare rápidamente.
Esto ayuda a prevenir reacciones de la batería de litio y el agua., Garantizar la sostenibilidad del efecto impermeabilizante..
Implementando estos métodos e incorporando medidas de impermeabilidad en los procedimientos de diseño y mantenimiento de la batería., Las baterías se pueden proteger eficazmente contra daños por agua..
Esto también garantiza su confiabilidad y seguridad en diversos escenarios de aplicación..
Para garantizar la seguridad y tranquilidad de tu batería de litio, es posible que desee comprobar el polímero de litio de alta calidad y Baterías de fosfato de hierro y litio proporcionadas por GycxSolar..
Obtenga más información sobre la seguridad de la batería y las mejores prácticas para proteger su inversión y mejorar el rendimiento de la batería..
Resumen

¿Las baterías de litio reaccionarán en agua?? En efecto, va a!
Si su batería de litio se moja accidentalmente, por favor no entre en pánico.
Tenga la seguridad de que varios productos de baterías GycxSolar tienen un alto nivel de protección de IP65, que puede resistir salpicaduras de agua.
Gracias a su estructura de sellado, Pueden evitar daños importantes o a largo plazo incluso en contacto directo con el litio en el agua..
Aunque la inmersión prolongada en agua puede plantear riesgos, Tomar las precauciones adecuadas puede garantizar el funcionamiento continuo y estable de la batería..
Con un desempeño sobresaliente, calidad incomparable, y excelentes estándares de seguridad, Las células GycxSolar son sin duda la opción preferida para aplicaciones de almacenamiento de energía..
Siempre estamos listos para brindarle soporte..
Nuestros equipos de ventas y servicio al cliente están siempre listos para responder sus consultas y brindar respuestas a sus preguntas.!
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Qué sucede cuando las baterías de litio se sumergen en el agua??
Si la batería de litio está completamente sumergida en agua, puede causar un cortocircuito interno, lo que provoca daños inmediatos y calentamiento de la batería.
Y debido a la reacción química entre el agua y los materiales internos de la batería., puede haber riesgo de incendio o explosión.
¿Las baterías de litio tienen propiedades impermeables??
Las baterías de litio no suelen tener función impermeable..
Debido a la falta de una carcasa protectora o un mecanismo de sellado para resistir la infiltración de humedad., Las baterías de litio son propensas a dañarse cuando se exponen a la humedad..
Cómo proporcionar protección impermeable para baterías de litio?
Equipe los dispositivos cargados con baterías de litio con carcasas impermeables o cubiertas protectoras..
Asegúrese de que la batería se almacene en condiciones secas., lejos de ambientes húmedos, y evitar reacciones del litio con agua.
En situaciones donde puede haber riesgo de contacto con la humedad., Se deben utilizar contenedores o bolsas impermeables para proteger la batería..
Evite situaciones con litio en agua..
