Les batteries rechargeables sont une partie très importante de notre vie moderne, Alimenter tout, des smartphones aux voitures électriques. Avec autant de types de batteries rechargeables sur le marché, Vous vous demandez peut-être quelle batterie rechargeable a la vie cyclable la plus longue.

Cet article nous emmènera plus profondément dans ce sujet, Comprendre les caractéristiques de différents types de batteries rechargeables à longue durée de vie, les facteurs clés qui affectent leur longévité, et quelles batteries sont les meilleures en termes de longévité.
Qu'est-ce qu'une batterie rechargeable?
UN batterie rechargeable est un type de batterie qui peut être rechargé et déchargé à plusieurs reprises par électricité. Contrairement aux batteries jetables, Les batteries rechargeables peuvent être utilisées plusieurs fois après avoir manqué de puissance en se connectant à un chargeur.

Il se compose d'une ou plusieurs cellules électrochimiques. Le terme « accumulateur » est utilisé car il accumule et stocke l’énergie grâce à des réactions électrochimiques réversibles.. Les batteries rechargeables sont disponibles dans une variété de formes et de tailles, Des batteries boutonnées aux systèmes de mégawatt connectés pour stabiliser les réseaux de distribution.
Quels sont les types de batteries rechargeables?
Il existe de nombreux types de batteries rechargeables sur le marché, chacun avec des caractéristiques et des applications uniques. La compréhension de ces différences vous aidera à choisir la meilleure batterie de longue durée pour vos besoins.
1. Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batterie
Caractéristiques: La batterie lithium-ion est connue pour leur densité d'énergie élevée, ce qui signifie qu'il peut stocker beaucoup d'énergie dans une taille et un poids relativement petites. Par conséquent, Les batteries au lithium-ion sont largement utilisées dans l'électronique grand public telles que les smartphones, ordinateurs portables et caméras.

Applications: Convient aux appareils électroniques portables, Véhicules électriques et systèmes de stockage d'énergie renouvelable.
Avantages:
Poids léger, facile à transporter.
Densité d'énergie élevée et endurance longue.
Faible taux d'autodécharge, Moins de perte de courant.
Inconvénient:
Il est sensible aux températures élevées et nécessite une bonne gestion thermique.
Risque de runnway thermique s'il est endommagé ou mal chargé.
2. Phosphate de fer et de lithium (LFP) batterie
Caractéristiques:Les batteries LFP sont un sous-type de batteries au lithium-ion connues pour leur sécurité et leur stabilité supérieures. Ils ont une densité d'énergie plus faible que les batteries au lithium-ion traditionnelles, Mais leur durée de vie est beaucoup plus longue.

Applications: Largement utilisé dans les véhicules électriques, Systèmes de stockage d'énergie solaire et outils électriques et autres champs.
Avantages:
Vie à service très longue, réduire la fréquence du remplacement.
Avec une stabilité thermique élevée et une stabilité chimique, une plus grande sécurité.
Fonctionne bien dans des conditions extrêmes.
Inconvénient:
La densité d'énergie est faible et le volume est relativement important.
Le coût initial est plus élevé, Mais le coût d'utilisation à long terme est plus faible.
3. Batteries au plomb
Caractéristiques: Les batteries au plomb sont l'un des plus anciens types de batteries rechargeables. Avec sa fiabilité et sa forte capacité de roulement de courant, Il est largement utilisé dans divers domaines.

Applications: Couramment utilisé dans les batteries de démarrage automobile, Alimentation sans interruption (UPS) systèmes, et solutions de stockage d'énergie solaire.
Avantages:
Fiabilité élevée et performance stable.
Peut résister au courant d'intrus élevé, Convient aux besoins élevés.
Faible coût, avantages économiques.
Inconvénient:
Grande taille et poids lourd, gênant à porter.
Un entretien régulier est requis, ce qui augmente la complexité.
La durée de vie est relativement courte et doit être remplacée fréquemment.
4.. Batterie d'hydrure de nickel en métal
Caractéristiques: Les batteries d'hydrure de nickel-metal sont une alternative plus sûre et plus respectueuse de l'environnement aux batteries au nickel-cadmium. En raison de sa fiabilité et de ses caractéristiques environnementales, Il est largement utilisé dans divers domaines de l'électronique ménagers aux véhicules hybrides.

Application: Convient à une variété de batteries rechargeables telles que l'électronique domestique, Véhicules hybrides et outils électriques.
Avantages:
Densité d'énergie modérée pour fournir une puissance stable.
Il est plus sûr que les batteries nickel-cadmium et ne contient pas de substances nocives.
Pas facile à produire l'effet de mémoire, durée de vie plus longue.
Inconvénient:
Taux d'auto-décharge élevé et temps de stockage court.
La chaleur est générée pendant le processus de charge, Alors faites attention à la dissipation de la chaleur.
En comprenant les caractéristiques de ces batteries rechargeables, Vous pouvez mieux peser leurs avantages et leurs inconvénients afin de mieux choisir le type de batterie qui convient le mieux à vos besoins, Assurer la meilleure expérience d'utilisation et la sécurité.
Quelle batterie rechargeable a la vie la plus longue?
Afin de déterminer quelle batterie à longue durée de vie a la plus longue durée de vie, Regardons de plus près la durée de vie des quatre types de batteries et comparons leurs caractéristiques.
1. Lithium-ion (Li-ion) durée de vie de la batterie
Gamme de vies: entre 300 et 500 cycles.
Les batteries au lithium-ion sont privilégiées en raison de leur densité d'énergie élevée et de leurs caractéristiques légères. Cependant, Même dans l'état inactif, Les performances des batteries lithium-ion se dégradent progressivement avec le temps en raison des réactions chimiques réalisées à l'intérieur de la batterie.
2. Phosphate de fer et de lithium (LFP) durée de vie de la batterie
Gamme de vies: 2000 à 5000 cycles.
Les batteries LFP sont connues pour leur longue durée de vie et une sécurité élevée. Par rapport à d'autres batteries lithium-ion, Ils sont stables à des températures élevées et moins sujettes à la fuite thermique. Bien que leur densité d'énergie soit faible, Leur longévité et leur stabilité les rendent idéaux pour les applications où la fiabilité à long terme est critique, comme les véhicules électriques et les systèmes de stockage d'énergie renouvelable.
3. Durée de vie de la batterie au plomb
Gamme de vies: Dans la gamme de 200 à 300 cycles
Les batteries au plomb sont robustes, stable et fiable, Mais avoir une durée de vie relativement courte. Pour maximiser la durée de vie, Des travaux d'entretien réguliers sont requis. Par exemple, Assurer les niveaux de charge appropriés tout en essayant d'éviter les décharges profondes. Si ce n'est pas correctement géré, sulfatation, Le processus par lequel les cristaux de sulfate de plomb se forment sur un panneau, peut réduire considérablement la durée de vie de la batterie.
4.Hydrure métallique de nickel (NiMH) durée de vie de la batterie
Gamme de vies: 500 à 800 cycles.
Les batteries d'hydrure de nickel-metal ont une durée de vie normale, et sont moins sujets aux effets de la mémoire qui affligent les batteries au nickel-cadmium plus anciennes. Cependant, Ils ont un taux d'auto-décharge plus élevé, ce qui signifie que leur pouvoir est perdu à un rythme plus rapide lorsqu'ils ne sont pas utilisés. La méthode de charge correcte peut aider à prolonger leur durée de vie.
| Type de batterie | Gamme de vies | Caractéristique principale |
| Plomb-acide | 200 à 300 | Lourd, fort, entretien, durée de vie courte |
| Lithium-ion (Li-ion) | 300 à 500 | Haute densité énergétique, poids léger, facile à dégrader |
| Batterie d'hydrure de nickel-metal (NiMH) | 500 à 800 | Densité d'énergie modérée, auto-décharge supérieure |
| Phosphate de fer au lithium (LFP) | 2000 à 5000 | Longue durée, stabilité élevée, densité d'énergie plus faible |
Ce qui détermine la durée de vie du cycle de batterie?
Il y a plusieurs facteurs qui peuvent affecter la durée de vie du cycle de batterie. Comprendre ces facteurs peut vous aider à maximiser la durée de vie de votre batterie.
Cycles de charge et de décharge
Le cycle de charge fait référence au processus pendant lequel une batterie est complètement chargée et déchargée. Chaque type de batterie peut être chargé un nombre limité de fois, au-delà de laquelle sa capacité baisse considérablement. La charge et la décharge fréquents affecteront la durée de vie globale de la batterie.
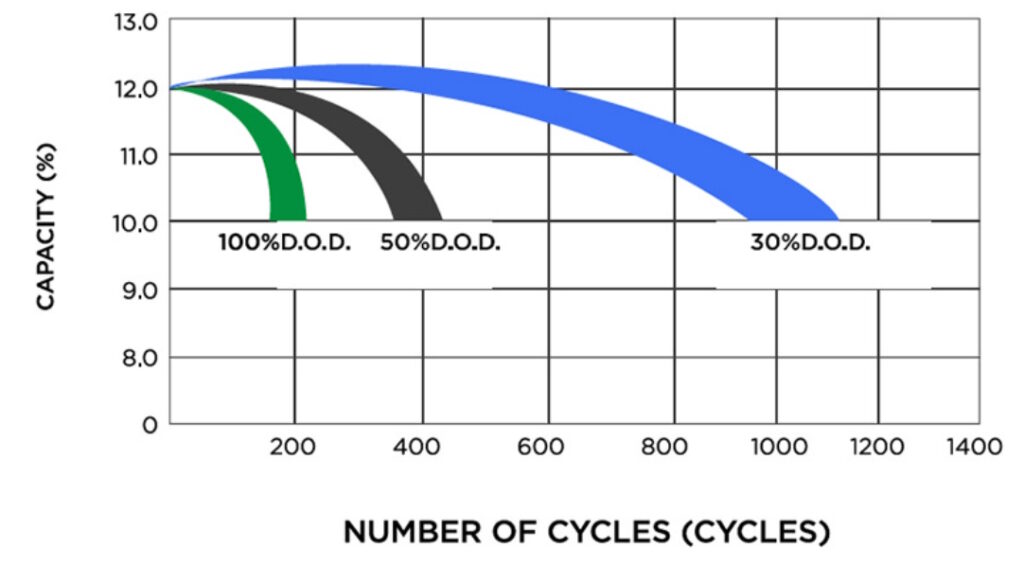
Température
Les températures extrêmement chaudes et extrêmement froides peuvent réduire les performances et la durée de vie de la batterie. Des températures élevées accéléreront les réactions chimiques à l'intérieur de la batterie, entraînant une perte de capacité, tandis que les basses températures réduiront l'efficacité et les performances de la batterie.
Modèle d'utilisation
La façon dont une batterie est utilisée et chargée affecte sa durée de vie. Des décharges profondes et des surcharges fréquentes peuvent réduire considérablement la durée de vie de la batterie.. Garder la batterie à l'état de charge moyen (entre 20% et 80%, Par exemple) peut prolonger sa durée de vie.
Maintenir
Un bon entretien peut considérablement prolonger la durée de vie de la batterie. Par exemple, Évitez la décharge complète et assurez-vous de stocker la batterie dans un cool, lieu sec. La vérification et l'équilibrage réguliers des cellules de la batterie aident également à prolonger la vie.
Chimie de batterie
Différents types de chimie de la batterie ont également des différences inhérentes à la durée de vie. Par exemple, Les batteries au lithium-ion ont généralement une durée de vie plus courte que le phosphate de fer au lithium (LFP) batteries, qui sont conçus avec plus d'accent sur la vie et la stabilité.
En comprenant et en gérant ces facteurs, Vous pouvez prolonger efficacement la durée de vie du cycle de la batterie et rendre ses performances plus durables et stables.
Plus la durée de vie du cycle des batteries rechargeables est-elle longue, le meilleur?
Bien que nous voulons généralement la durée de vie du cycle de la batterie aussi longtemps que possible, Ce n'est pas le seul facteur à considérer lors du choix d'une batterie. Voici quelques points clés à garder à l'esprit pour vous aider à prendre une décision plus holistique.

Coût
Note: Batteries avec une longue vie (comme les batteries LFP) ont généralement un coût initial plus élevé. Vous devez évaluer si la durée de vie plus longue vaut l'investissement initial plus élevé en fonction de l'utilisation et du budget réels.
Performance
Note: Les batteries qui durent plus longtemps peuvent avoir une densité d'énergie plus faible. Cela signifie qu'ils sont capables de stocker moins d'énergie et peuvent ne pas être optimaux pour les applications qui nécessitent un poids léger et une densité d'énergie élevée.
Exigence de demande
Note: La meilleure batterie pour votre application dépend de plus que de la vie. Par exemple, Pour les appareils qui doivent être légers et portables, La densité d'énergie élevée comme les batteries au lithium-ion peut être plus importante que la durée de vie à cycle long.
Implication environnementale
Note: Certaines batteries sont plus respectueuses de l'environnement que d'autres. Par exemple, Les batteries d'hydrure de nickel-metal sont moins toxiques, tandis que les batteries au plomb nécessitent une manipulation soigneuse. Choisir des batteries avec une durée de vie plus longue peut également aider à réduire les déchets et l'impact environnemental.
Conclusion
En bref, Si vous cherchez une batterie rechargeable avec la vie la plus longue, puis au lithium en phosphate de fer (LFP) Les batteries sont sans aucun doute le meilleur choix. Avec un excellent 2,000 à 5,000 Cycle de vie, Ils sont idéaux pour les applications où l'espérance de vie est extrêmement élevée.
Cependant, Lors du choix d'une batterie, Il est tout aussi important d'équilibrer plusieurs facteurs tels que la vie, coût, Performances et besoins spécifiques à l'application. Chaque type de batterie de longue durée de vie a ses avantages et ses inconvénients. Le meilleur choix dépend des fonctionnalités que vous appréciez le plus lorsque vous utilisez votre batterie. En acquiant un aperçu des différents types de batteries rechargeables et des facteurs qui affectent leur longévité, Vous pouvez prendre une décision éclairée qui convient le mieux à vos besoins.
