I circuiti delle batterie sono il cuore dei dispositivi elettronici contemporanei, alimentare gli strumenti essenziali della vita moderna.
Insieme, esploreremo di cosa sono fatti, cosa fanno, e le considerazioni che vanno nella loro progettazione.
Con conoscenza dei circuiti della batteria, possiamo progettare circuiti per impianti fotovoltaici efficienti ed affidabili.
Concetti base sui circuiti di batteria
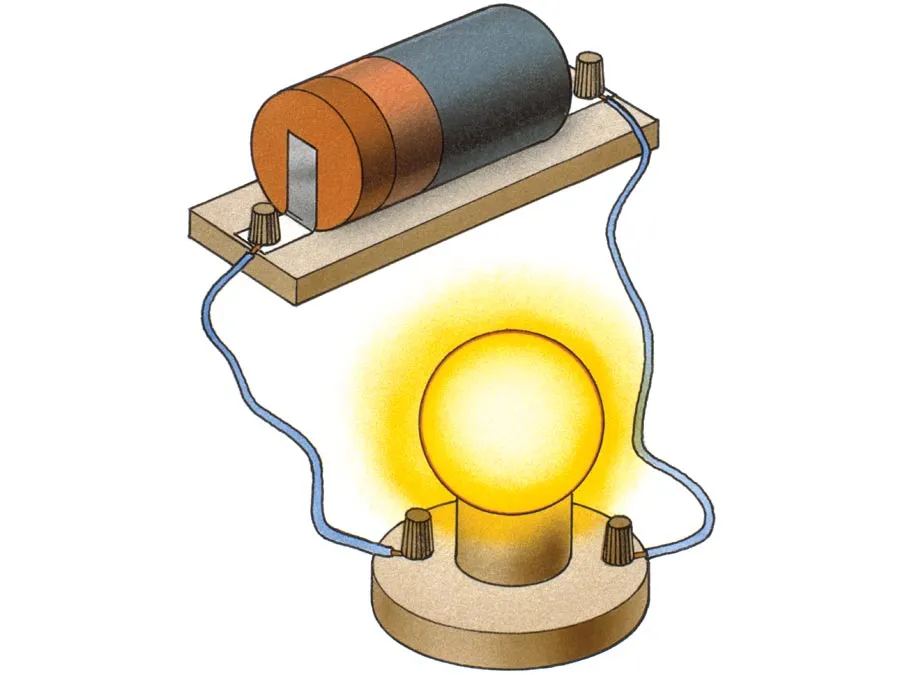
Definizione di circuito
Un circuito è un percorso chiuso che consente il flusso di corrente ed è composto da componenti interconnessi come fonti di alimentazione, conduttori, e carichi.
La sua funzione è quella di fornire energia elettrica ad apparecchiature e sistemi di alimentazione.
Un circuito batteria è un dispositivo di base che trasferisce energia elettrica da una fonte di alimentazione (come una batteria) ad un carico attraverso componenti conduttivi e varie parti.
Questo tipo di dispositivo svolge un ruolo cruciale in numerosi dispositivi e sistemi elettronici.
Prossimo, forniremo un’analisi dettagliata delle sue componenti principali:
Batteria
Come fonte di energia, una batteria è una fonte di energia chimica in grado di fornire energia elettrica in modo indipendente. Converte l'energia chimica in energia elettrica attraverso reazioni chimiche.
Le batterie possono essere composte da celle elettrochimiche singole o multiple collegate in serie o parallelo.
Ogni batteria include un elettrodo positivo (catodo), un elettrodo negativo (anodo), e un elettrolita, che promuove il movimento degli ioni tra gli elettrodi positivi e negativi nelle reazioni elettrochimiche.
Carico
Il carico dell'apparecchiatura che consuma energia elettrica si riferisce ai componenti o ai dispositivi che utilizzano energia elettrica per completare attività specifiche.
Può includere apparecchiature di illuminazione, motori elettrici, microprocessori, o qualsiasi apparecchio elettrico che fa affidamento sull'elettricità per il funzionamento.
Il carico è collegato al circuito della batteria per ottenere e consumare energia elettrica.
Componenti conduttivi
I materiali conduttivi come i fili, morsettiere, e il cablaggio su circuiti stampati che trasmettono corrente funge da percorso per il flusso della corrente dalla batteria al carico e ritorno.
Questi componenti assicurano che la corrente scorra lungo un percorso a bassa resistenza, riducendo efficacemente la perdita di energia nel circuito.
Interruttori e dispositivi di controllo
Interruttori e componenti di controllo sono spesso installati nei circuiti delle batterie. L'interruttore consente agli utenti di controllare l'accensione/spegnimento della corrente, controllando così l'avvio e l'arresto del circuito.
Componenti di controllo come resistori o transistor possono regolare il livello di corrente o tensione all'interno di un circuito.
Dispositivi di protezione
Componenti di protezione come fusibili o interruttori automatici vengono utilizzati per proteggere i circuiti dai danni causati da sovraccarico o cortocircuiti.
Questi dispositivi possono proteggere i dispositivi nella batteria e nel circuito da potenziali danni causati da picchi di corrente anomali.
Strumenti di monitoraggio e misurazione
In sistemi di circuiti batteria più complessi, strumenti di monitoraggio e misurazione come voltmetri, amperometri, oppure possono essere inclusi multimetri.
Questi strumenti consentono agli operatori di monitorare parametri elettrici come tensione e corrente nel circuito, fornendo dati diagnostici critici per le prestazioni del circuito.
Il principio di funzionamento del circuito della batteria
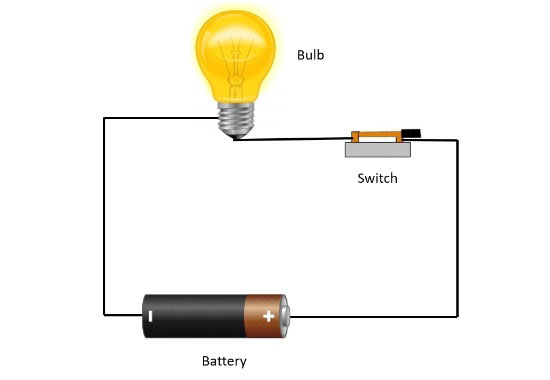
Il rapporto tra batterie e circuiti:
La batteria stessa non è un circuito, ma un'unità di accumulo dell'energia elettrica.
Molte persone potrebbero essere confuse riguardo al concetto di circuiti batteria, ma dovrebbe essere chiaro che le batterie stesse non sono circuiti.
Una batteria è un dispositivo di accumulo di energia in grado di fornire energia elettrica.
Gli elementi costitutivi del circuito della batteria:
Il circuito della batteria è costituito da diversi componenti di base che lavorano insieme per facilitare il flusso di corrente ed energia elettrica tra i dispositivi.
Questi componenti includono:
Batteria:
Come fonte di energia potenziale elettrica. Converte l'energia chimica in energia elettrica attraverso reazioni chimiche e può essere composto da celle di batteria singole o multiple.
Le batterie al litio sono uno dei tipi più comuni di batterie.
Caviera:
Il canale che costituisce il flusso della corrente elettrica.
I cavi collegano la batteria ad altri componenti nel circuito, permettendo agli elettroni di fluire attraverso di essi.
Interruttore:
Utilizzato per controllare la connessione e la disconnessione dei circuiti.
Resistori:
Regolare il flusso di corrente nel circuito e regolare il livello di tensione in base alla domanda.
Carico:
Convertire l'energia elettrica in altre forme come la luce, movimento, o elaborazione dati.
Il carico comprende tutti i dispositivi che consumano energia elettrica, come le lampadine, elettrodomestici, e motori.
Il meccanismo di funzionamento del circuito della batteria:
Nel buon funzionamento dei circuiti della batteria, ci sono diversi passaggi chiave che promuovono il flusso di corrente:
Migrazione elettronica:
Gli elettroni con carica negativa si spostano dal polo negativo al polo positivo della batteria. Questa migrazione è causata dalla differenza di potenziale generata dalle reazioni chimiche interne alla batteria.
Percorso conduttivo:
I componenti conduttivi come fili o cablaggi sul circuito forniscono un percorso per la propagazione degli elettroni.
Percorso a bassa impedenza:
Questi percorsi forniscono percorsi di flusso a bassa impedenza per gli elettroni, garantendo un flusso efficiente di elettroni.
Interazione con il carico:
Elettronica e carichi si incontrano, e il carico potrebbe essere una lampadina, un motore elettrico, o qualsiasi dispositivo all'interno del circuito.
Trasferimento di energia al carico:
Gli elettroni trasferiscono energia al carico, fornendo alimentazione ai dispositivi collegati.
Corrente continua:
Il flusso continuo di elettroni lungo un percorso conduttivo genera una corrente elettrica.
Intensità attuale:
La portata della corrente ne determina l'intensità, che si misura in ampere (UN).
Circuito chiuso:
Il circuito chiuso del circuito garantisce il flusso continuo di elettroni.
Reazione chimica:
Le reazioni chimiche all'interno della batteria guidano la migrazione degli elettroni. Queste reazioni generano una differenza potenziale, fornendo energia per il flusso di elettroni.
Quali sono i parametri chiave dei circuiti della batteria?
Alcuni parametri svolgono un ruolo cruciale nella progettazione e nel funzionamento dei circuiti delle batterie.
Padroneggiare questi parametri è essenziale per costruire sistemi di circuiti efficienti e ottimizzati.
I parametri principali sono:
Voltaggio:
La differenza di potenziale fornita dalla batteria è la forza che guida il flusso di corrente nel circuito.
L'unità è volt (v).
Corrente elettrica:
La quantità di carica che scorre nel circuito determina la velocità con cui l'energia elettrica viene trasmessa al carico.
L'unità è Ampere (UN).
Resistenza:
Misurare il grado di ostruzione al flusso di elettroni in un circuito, in ohm (OH).
Può essere una proprietà intrinseca del componente o aggiunto intenzionalmente per controllare la corrente.
Capacità:
La quantità di energia elettrica che una batteria può immagazzinare, misurato in ampere-ora (Ah).
Influisce sulla durata dell'alimentazione della batteria al carico.
Voltaggio, attuale, e resistenza nei circuiti della batteria
Voltaggio:
Definizione: La differenza di potenziale tra due punti di un circuito, misurato in volt (v).
Influenza:
Una tensione più elevata significa che ciascuna cella della batteria può fornire più energia, influenzando la potenza complessiva.
La tensione è la forza che spinge gli elettroni attraverso un circuito.
Corrente elettrica:
Definizione: La velocità del flusso di carica, misurato in ampere (UN).
Effetto:
L'intensità del flusso elettronico determina l'efficienza operativa dell'apparecchiatura.
La corrente elevata può fornire una potenza maggiore alle apparecchiature, ma potrebbe anche danneggiare i componenti.
Resistenza:
Definizione: L'ostruzione del flusso di elettroni, misurato in ohm (OH).
Influenza:
Un aumento della resistenza limiterà la corrente e influenzerà le prestazioni del circuito.
Componenti come resistori o materiali conduttivi possono influenzare la resistenza totale.
La legge di Ohm
Descritto il rapporto tra voltaggio (v), attuale (IO), e resistenza (R):
V = VAI.
Fornite le equazioni fondamentali per l'analisi circuitale.
Dissipazione di potenza:
La combinazione di tensione e resistenza determina la dissipazione di potenza in un circuito.
Maggiore è la tensione attraverso l'elemento resistore, maggiore è la potenza dissipata, che potrebbero compromettere la durata dell'elemento.
Classificazione dei circuiti delle batterie
È una batteria equivalente a un circuito elettrico? Qual è la differenza tra batterie e circuiti?
Una batteria non è equivalente a un circuito elettrico, ma piuttosto una parte del circuito che funge da fonte di energia.
Il circuito copre l'intero percorso del flusso di corrente, compresa la batteria.
La batteria stessa è un dispositivo che immagazzina e fornisce energia potenziale elettrica.
Quando una batteria diventa parte di un circuito elettrico, converte l'energia chimica immagazzinata all'interno in energia elettrica.
Circuito batteria in serie
Un circuito in serie crea un unico percorso di flusso di corrente collegando più batterie o componenti end-to-end.
In questa configurazione di serie, il polo positivo della batteria è collegato al polo negativo della batteria successiva, formando una catena in serie continua.
In un circuito in serie, tutti i componenti o le batterie condividono la stessa corrente, ma la tensione aumenta con il numero di componenti in serie.
Caratteristiche e vantaggi includono:
Corrente stabile:
La corrente rimane costante mentre scorre attraverso ciascun componente collegato in serie.
Tensione accumulata:
La tensione totale di un circuito in serie è la somma delle tensioni di tutti i componenti, che può fornire un'uscita di tensione più elevata.
Distribuzione uniforme della corrente:
Ogni componente è distribuito uniformemente con la stessa corrente per garantire un funzionamento bilanciato.
Equilibrio di tensione:
Per applicazioni che richiedono alta tensione ma bassa richiesta di corrente, i circuiti in serie sono particolarmente adatti.
Circuito batteria parallelo
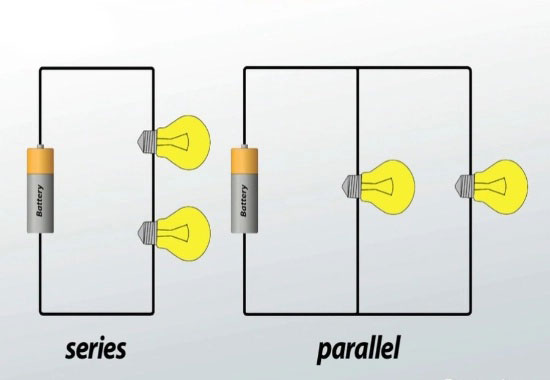
I circuiti paralleli collegano batterie o componenti fianco a fianco, con ciascun componente avente un percorso di flusso di corrente indipendente.
In una configurazione parallela, i poli positivo e negativo di tutti i componenti o delle batterie sono collegati separatamente.
In un circuito parallelo, ogni componente o batteria riceve l'intera tensione dell'alimentatore.
Caratteristiche e vantaggi includono:
Percorsi di corrente multipli:
La corrente è distribuita tra i rami paralleli, fornendo percorsi di corrente indipendenti per diversi componenti.
Tensione unificata:
Tutti i componenti godono della stessa tensione dell'alimentatore, garantire la costanza delle prestazioni.
Design ridondante e alta affidabilità:
Anche se un componente si guasta, altri componenti possono ancora funzionare in modo indipendente, migliorare l’affidabilità complessiva del sistema.
Maggiore capacità di corrente:
Il metodo di connessione in parallelo può raggiungere una capacità di corrente totale maggiore ed è adatto per applicazioni con elevate richieste di potenza.
Principio di funzionamento del circuito batteria
①Circuito della batteria durante il processo di ricarica
Il circuito controlla il flusso ordinato di corrente nella batteria per immagazzinare energia elettrica.
Il caricabatterie fornisce una tensione superiore alla tensione interna della batteria, facendo sì che gli elettroni fluiscano dal caricabatterie al polo positivo della batteria.
Durante la ricarica della batteria, le reazioni chimiche interne vengono attivate per ripristinare la sua energia potenziale elettrochimica.
②Circuito della batteria durante il processo di scarica
Quando la batteria è scarica, il circuito della batteria lo collega al dispositivo di carico.
Il circuito garantisce che la corrente fluisca dalla batteria al carico, fornire l’energia elettrica necessaria per il funzionamento dell’apparecchiatura.
La reazione chimica all'interno della batteria genera una differenza di potenziale tra i due poli, e il circuito consente agli elettroni di spostarsi dal polo negativo al polo positivo, fornire alimentazione al carico.
Durante il processo di dimissione, la reazione chimica della batteria consumerà l'energia immagazzinata.
Cos'è un circuito di protezione della batteria?
Le batterie al litio sono protette da circuiti di protezione della batteria per prevenire potenziali rischi come il sovraccarico, scarica eccessiva, o corrente eccessiva.
Include molte funzionalità di sicurezza, sensori di temperatura, limitatori di corrente, e regolatori di tensione.
Questi componenti controllano e monitorano il processo di carica e scarica della batteria per garantire un funzionamento sicuro e ottimale.
Principi di progettazione del circuito della batteria
Per creare un circuito batteria ad alte prestazioni, è necessario bilanciare attentamente numerosi elementi di design.
Questi elementi includono il livello di tensione richiesto dal carico, le caratteristiche di lavoro del carico, la capacità di carico dei componenti, necessarie misure di sicurezza, e la durata prevista della batteria.
Quando si progettano circuiti di batterie, il primo passo è valutare la richiesta di potenza del carico e selezionare batterie con tensione e capacità sufficienti.
Allo stesso tempo, il tasso di scarico, composizione chimica, È necessario considerare anche l'ambiente circostante la batteria.
È necessario garantire che tutti i componenti del circuito della batteria, compresi i fili, interruttori, e resistori, può sopportare il carico di corrente previsto ed evitare problemi come surriscaldamento o caduta di tensione.
I progettisti professionisti di GycxSolar personalizzerà per te tutti i circuiti del tuo sistema di accumulo dell'energia solare. Vieni e provalo.
Guida alla manutenzione del circuito e alla risoluzione dei problemi
Fasi di manutenzione per il circuito della batteria:
Ispezionare regolarmente l'aspetto dei terminali della batteria per garantire che non siano presenti sporco o corrosione.
Controllare se i cavi e i punti di connessione sono usurati o danneggiati, e ripararli o sostituirli se necessario.
Monitoraggio della tensione:
Controllare regolarmente la tensione della batteria utilizzando un voltmetro per mantenerla entro l'intervallo appropriato.
Prestare attenzione ad eventuali fluttuazioni anomale o diminuzioni di tensione, che potrebbe essere un segno di un problema.
Pulizia e manutenzione:
Pulisci i terminali della batteria e le parti di collegamento con una soluzione di bicarbonato di sodio per rimuovere la corrosione.
Conservare la batteria in un luogo pulito e asciutto per evitare contaminazione e danni dovuti all'umidità.
Ricarica corretta:
Seguire le raccomandazioni di ricarica del produttore per evitare di sovraccaricare o sottocaricare la batteria.
Utilizzare un caricabatterie adatto e seguire il tempo di ricarica consigliato per preservare la salute della batteria.
Tecniche di diagnosi dei guasti:
Identificare le anomalie di tensione:
Utilizzare un multimetro per rilevare la caduta di tensione nel circuito e identificare l'area problematica.
Testare ciascun componente per determinare se provoca una caduta di tensione o un'anomalia.
Individuazione dei problemi attuali:
Misurare la corrente nel circuito e identificare anomalie o cambiamenti improvvisi.
Identificare i componenti con elevato consumo di corrente, che potrebbero indicare guasti o degrado delle prestazioni.
Risolvere il problema della resistenza:
Testare la resistenza di ciascuna parte del circuito e identificare le aree con elevata resistenza.
Controllare i componenti o le connessioni che provocano un aumento della resistenza e compromettono l'efficienza.
Isolamento dei componenti difettosi:
Identificare i componenti difettosi utilizzando metodi di test del sistema.
Sostituire o riparare i componenti difettosi per garantire il funzionamento ottimale del circuito.
Domande frequenti

Cos'è un circuito di protezione della batteria?
Le batterie al litio sono protette da circuiti di protezione della batteria per prevenire potenziali rischi come il sovraccarico, scarica eccessiva, o corrente eccessiva.
Include molte funzionalità di sicurezza, sensori di temperatura, limitatori di corrente, e regolatori di tensione.
Questi componenti controllano e monitorano il processo di carica e scarica della batteria per garantire un funzionamento sicuro e ottimale.
Cos'è un circuito di sostituzione della batteria?
Un circuito di sostituzione della batteria è una fonte di alimentazione in grado di fornire una tensione CC stabile a dispositivi o circuiti, riducendo o eliminando così la dipendenza dalle batterie.
Questo tipo di circuito utilizza in genere un adattatore di alimentazione per simulare le caratteristiche di alimentazione di una batteria.
La batteria forma un circuito semplice?
Non è così, le batterie stesse non equivalgono a un circuito completo.
Come fonte di energia, le batterie devono funzionare insieme ad altri componenti del circuito come i cavi, interruttori, e carichi per formare un sistema di circuito completo che consenta il flusso di corrente.
Quanta corrente fornisce la batteria?
Il termine “batteria” qui si riferisce a un’energia potenziale elettrica che può fornire continuamente un flusso di carica, permettendo alla corrente di passare attraverso il circuito.
Le batterie sono la fonte di energia che guida il flusso di corrente nei circuiti.
Un cortocircuito causerà danni alla batteria?
Infatti, un cortocircuito potrebbe causare un aumento di corrente e danneggiare la batteria.
Un cortocircuito può generare una grande quantità di calore, che potrebbero causare perdite di elettrolito all'interno della batteria, danni ai componenti interni, e in casi estremi possono addirittura portare alla rottura della batteria.
