Voltage and current are fundamental concepts in electrical engineering.
Understanding what is the difference between volts and current is crucial for a profound understanding of the operation of electricity.
This article will explore the knowledge of voltage and battery current, covering definitions and difference between current & voltage.
It will be very helpful for those in need.
What is voltage?
Battery voltage refers to the electromotive force (EMF) generated by a battery, also known as the potential difference or potential difference.
Voltage is used to measure the potential energy that expresses a unit charge, essentially the force that propels current through a conductor.
The unit of voltage is volts (V), defined as the energy of one joule per coulombic charge.
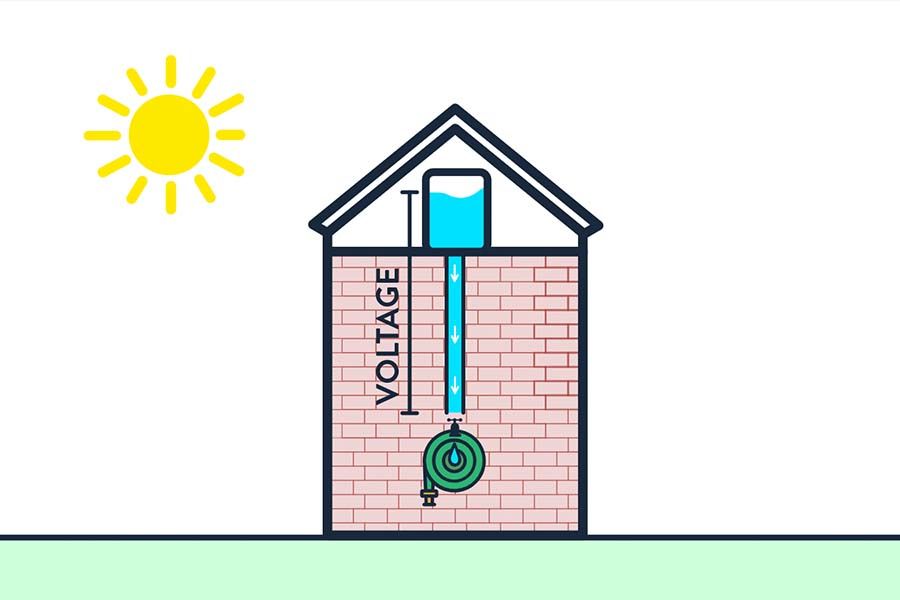
Voltage can be likened to the water pressure of a water pipe.
Just as water flows from high water pressure areas to low water pressure areas, current also flows from high voltage points to low voltage points.
The larger the voltage difference, the more energy is available to drive the current through the circuit.
When discussing battery voltage, we are actually exploring the potential energy difference between the positive and negative electrodes of the battery.
This difference generates an electric field, which promotes the flow of electrons.
Thus achieving the transmission of electrical energy from the battery to the connected devices, providing the necessary energy for electronic devices.
What is battery current?
Current refers to the movement of charge in a circuit, which defines the amount of charge passing through a certain point in the circuit per second.
The current in a circuit is generated by the movement of electrons (negatively charged particles).
These electrons flow through the circuit under the drive of voltage difference, from the negative pole of the voltage source to the positive pole, forming a closed circuit.
Thus achieving energy transmission and providing power for electronic components in the circuit.
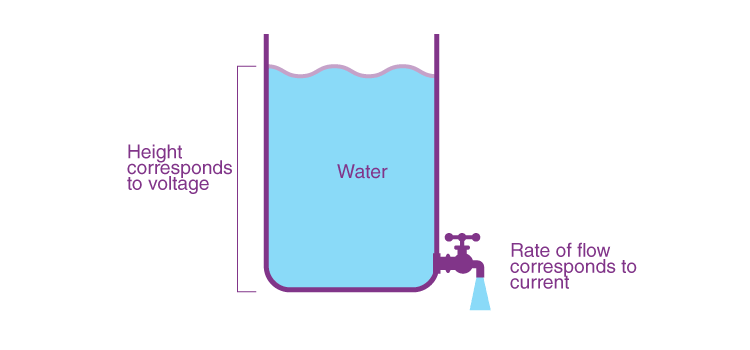
Electric current can be analogized to the velocity of water flow in a pipeline.
The speed of water flow is measured in gallons per minute, while the speed of electric current is measured in amperes.
The unit of current is ampere (A), usually represented by the symbol “I”.
The speed at which current passes through a circuit depends on the applied voltage and the resistance of the circuit.
The magnitude of current is directly proportional to the voltage (V) in the circuit and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) in the circuit.
The higher the voltage or the lower the resistance, the greater the current.
What is the difference between voltage and current?
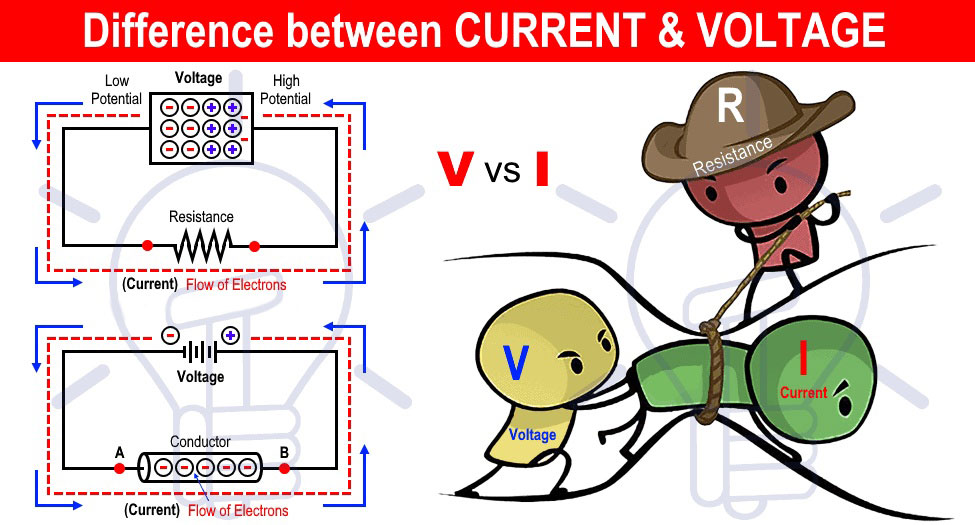
Although voltage and current are interrelated, they play different roles in electrical systems.
Mastering the difference between these two is crucial for a deeper understanding of the working principles and functions of circuits.
Here is the difference between current & voltage:
Definition difference:
Voltage is a measure of the potential energy per unit charge, known as the potential difference.
It is the driving force that causes the flow of electric current, measured in volts (V).
Current is the actual movement of charge in a circuit, measured in amperes (A).
Symbol representation:
Voltage is commonly represented by “V”.
Current is commonly represented by “I”.
Physical property:
Voltage is a scalar, with only magnitude and no direction.
Current is a vector, with both magnitude and direction.
Functional role:
Voltage is the driving force that propels current through an electrical circuit.
It provides energy for the movement of electrons in circuits.
Current is the manifestation of the actual flow of electrons.
Measuring instrument:
Voltage is measured through a voltmeter.
The current is measured through an ammeter.
Dependence:
Voltage is independent of the circuit, while the magnitude of current is influenced by the resistance of the circuit.
They are different physical quantities.
Voltage generates an electric field, which promotes the flow of current.
The magnitude of the current depends on the applied voltage and the resistance of the circuit.
Now you understand what is the difference between volts and current.
What you will learn next is how is current and voltage related and how they influence each other.
Ohm’s Law:
Mathematically, Ohm’s law is expressed as I=V/R
I represents current (unit: ampere, A)
V represents voltage (unit: volt, V)
R represents resistance (unit: ohm, Ω)
Ohm’s Law elucidates the fundamental relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
It indicates that the current in a circuit is proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance.
Proportional relationship:
Through Ohm’s Law, you will know that there is a proportional relationship between voltage and current.
Through Ohm’s Law, you will know that there is a proportional relationship between voltage and current.
For example, if the voltage across the circuit doubles while the resistance remains constant, the current flowing through the circuit will also double.
The influence of resistance:
The change in resistance will alter the relationship between voltage and current.
When the voltage is constant, if the resistance increases, the current will decrease.
Because higher resistance restricts the flow of electrons.
On the contrary, if the voltage remains constant and the resistance decreases, the current will increase.
Because the lower resistance reduces the obstruction of electron flow.
Power calculation:
Voltage and current are crucial for calculating power in a circuit.
Power is measured in watts (W) and is the product of voltage and current: P=V * I.
This relationship highlights the importance of voltage and current in determining the energy consumption or transmission of a circuit.
Series and parallel circuits:
In a series circuit, voltage is distributed among various components, but the current of the entire circuit is the same.
In a series circuit, voltage is distributed among various components, but the current of the entire circuit is the same.
In a parallel circuit, the voltage of each branch is the same, while the total current is distributed among the various components.
The sum of the currents in each branch is equal to the total current entering the circuit.
Conclusion
In summary, voltage and current are important fundamental concepts that make up an electrical system.
Voltage measures the potential energy of a unit charge, while current describes the flow of charge in a circuit.
Mastering the differences in voltage and current and their interactions is essential for circuit design and analysis, power supply for electronic devices, and ensuring electrical safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will there still be voltage without current?
In fact, voltage can exist independently of current.
Voltage is a measure of potential difference, which represents the potential to drive current flow.
However, without a closed circuit providing a path, even if there is a voltage difference, electrons cannot flow.
This way, there will be no current generated.
In short, voltage is a necessary condition for the flow of current, but the flow of current also requires a complete circuit path.
What is the difference between the concepts of current and electricity?
Current specifically refers to the flow of electric charge, measured in amperes (A).
Electricity is a broader concept used to describe various phenomena related to the flow of electric charges.
Current refers to the flow of electrons in a circuit, while electricity encompasses the entire range of electrical phenomena and their applications.
What problems can high voltage cause?
When the voltage in the circuit exceeds the normal range, it may cause a series of negative effects.
Excessive voltage may cause circuit components to overheat, damage, and even pose a risk of electric shock.
If it is a high-voltage battery, it may pose more potential risks during use.
The safety of GycxSolar lithium batteries has been certified by authoritative testing institutions, making it your reliable choice.
