Do Lithium Batteries Leak?
The answer is that there is a small chance of battery leakage.
Lithium ion batteries have become an indispensable source of energy for many of our daily devices, such as smartphones and electric vehicles. People generally worry about will lithium batteries leak during use.
In this article, we will delve into the leakage issues of lithium-ion batteries, including the causes, impacts, and preventive measures to ensure their safe use.
Part 1. What is a lithium battery leak?

Battery leakage refers to the situation where the battery casing ruptures, causing the internal electrolyte to leak out. Electrolyte is a corrosive and flammable chemical mixture that may pose a danger upon contact with skin or flammable materials.
There are many situations that can cause battery leakage, such as manufacturing defects, improper use, or short circuits, including physical impacts on the battery or production defects.
Lithium ion batteries are rechargeable power sources that store and release energy through the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode. This type of battery usually consists of a positive electrode, a negative electrode, and an electrolyte.
Once a lithium-ion battery leaks, it may cause problems such as electrolyte evaporation, water infiltration, and battery expansion. These problems not only reduce the performance of the battery, but may even lead to fire or explosion in severe cases.
Part 2. Why does battery leak?
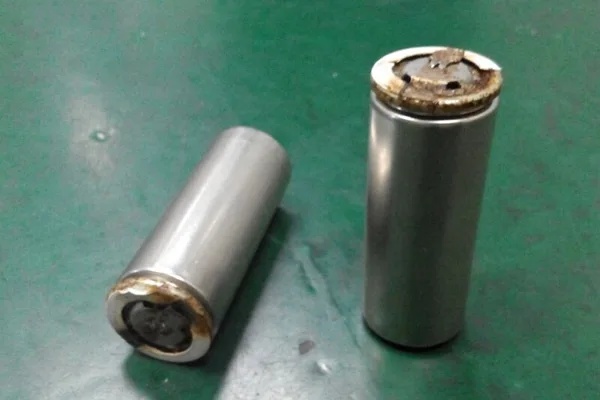

Lithium ion batteries are usually not prone to leakage, but under certain conditions, leakage may still occur.
Here are some possible causes of liquid leakage:
Physical damage
If there is physical damage to the battery, such as external impact or compression, or it may be pierced or deformed, it may damage the integrity of its shell and cause battery leakage.
If there is physical damage to the battery, such as external impact or compression, or it may be pierced or deformed, it may damage the integrity of its shell and cause battery leakage.
This test is used to evaluate the durability of batteries and their ability to withstand damage. Choosing a reputable brand, such as GycxSolar, can provide batteries with stronger anti leakage performance and protect your investment costs.
Manufacturing quality
Poor quality manufacturing processes, such as inadequate sealing or improper assembly of battery components, may result in quality issues and ultimately lead to battery leakage.
Therefore, when choosing lithium batteries, it is crucial to choose a reputable manufacturer. GycxSolar’s LiFePO4 lithium batteries have passed multiple certification tests including UL, FCC, CE, RoHS, and UN38.3.
Improper use
Improper use of batteries, such as overcharging or discharging, can cause damage to the battery, which may damage the internal separator and lead to battery fluid leakage.
If lithium batteries are overcharged, it may cause overheating and pressure accumulation. If the battery quality cannot effectively control these situations, it may lead to leakage.
Environmental impact
If the battery is kept in a humid environment for a long time, it may cause internal short circuits, which may lead to battery fluid leakage.
If lithium batteries are exposed to high temperatures or extreme temperatures for a long time, their internal electrolytes may be damaged, increasing the risk of battery leakage. So it is very important to store lithium batteries in a cool and dry place.
Following GycxSolar’s storage guidelines can help minimize the risk of battery leakage to the greatest extent possible.
The impact of battery aging and battery accessories
As the battery is used for a long time or at a high frequency, it will gradually age and its internal chemical components will gradually dissolve.
The decrease in stability of internal materials can lead to a decrease in battery performance and even possible leakage.
If the battery is disassembled or modified improperly, it may damage the internal structure of the battery and cause leakage.
And using non original battery accessories, such as inferior chargers for charging, may cause battery overheating and leakage due to high voltage and current.
Part 3. Types of batteries that are prone to leakage
Lithium ion batteries can provide powerful power, but they are prone to breakage and battery leakage when subjected to impact or improper operation.
Lithium polymer batteries use different electrolytes and are typically used in medical devices and electronic cigarettes. Like lithium-ion batteries, due to their fragility, they may also leak if damaged or broken.
Which type of lithium battery is least prone to leakage?
Among various types of lithium batteries, lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are considered the least prone to leakage. Because they use iron instead of cobalt in the electrolyte of their internal structure.
However, compared to other rechargeable batteries, their power output and lifespan are usually shorter.
The latest innovation is lithium sulfur batteries. These types of batteries are more environmentally friendly because they use sulfur instead of lithium in the manufacturing process.
Compared to other lithium batteries, their leakage risk is relatively low.
For specific comparisons, please refer to this article by GycxSolar: Lithium Sulfur Battery vs Lithium ion Battery – How to Choose
Part 4. What are the potential hazards of lithium battery leakage?
Damage to electronic devices
The electrolyte released when a lithium battery leaks is corrosive and may cause damage to electronic devices. This corrosion may cause equipment malfunction and even irreversible damage.
Risk of fire and explosion
Lithium batteries contain highly active and flammable substances such as lithium and organic solvents. Once the battery leaks, lithium comes into contact with moisture or other active substances.
If the leaked electrolyte comes into contact with flammable substances, it may cause a fire or explosion.
Leakage of lithium batteries may also cause thermal runaway, and the accumulated heat may lead to spontaneous combustion or explosion of the battery.
If the battery experiences a short circuit or is exposed to high temperatures and damaged, this situation is particularly dangerous.
If the lithium battery leaks and causes a short circuit in the equipment, resulting in equipment failure and posing electrical safety risks.
Continuing to use damaged equipment will cause it to stop working, which is extremely unsafe. There may also be risks such as fire and electric shock.
Chemical hazards
Toxicity issue:
Lithium batteries contain electrolytes and other chemicals, such as lithium salts, organic solvents, and heavy metals produced in some cases. If a leak occurs, these substances may pose a threat to human health.
Direct contact with these chemicals may cause skin irritation, chemical burns, or more serious health problems.
Smoke and steam:
Leaked lithium batteries can release harmful gases and vapors, such as hydrofluoric acid (HF) and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which may be toxic when inhaled.
Long term exposure to these fumes may cause respiratory irritation and even lung damage.
To minimize these risks to the greatest extent possible, handle leaking lithium batteries with caution.
It is crucial to purchase high-quality batteries from reputable suppliers and follow the correct charging and usage guidelines.
If a battery leak occurs, appropriate protective equipment should be worn and the correct cleaning and disposal procedures should be followed to ensure safety.
Causing harm to health:
①Skin and eye irritation:
If the leaked battery electrolyte comes into direct contact with the skin or eyes, it may cause burns, irritation, or serious injury, especially when the electrolyte contains hydrofluoric acid or other corrosive components.
②Respiratory system issues:
Inhaling smoke generated by leaking batteries may cause irritation to the lungs and respiratory tract.
Exposure to toxic gases may even lead to more serious health problems, such as difficulty breathing or lung damage.
③Risk of corrosive substances:
The electrolyte in lithium batteries is usually corrosive. Once a leak occurs, it may not only damage the surface of the item and corrode the metal, but also cause chemical burns and harm to the body.
Therefore, it is necessary to avoid direct contact with leaked electrolyte and take appropriate safety precautions.
Environmental hazards
Soil and water pollution:
If the chemicals in lithium batteries (such as lithium salts and other toxic substances) are not properly treated, they may seep into the soil and water.
This type of pollution may pose a threat to wildlife and the entire ecosystem, and may even affect human drinking water sources.
Hazardous waste disposal:
Leaked or damaged lithium batteries should be managed as hazardous waste and disposed of safely in accordance with relevant regulations to prevent further damage to the environment.
Part 5. How to check lithium batteries are leaking?
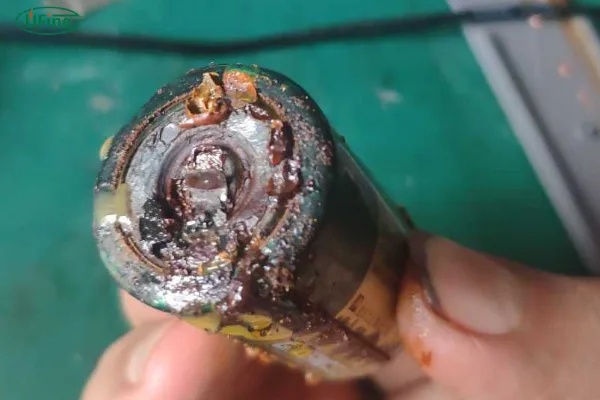

To determine if a lithium battery is leaking, please follow the steps below for inspection:
Visual observation
Carefully observe the battery and look for any obvious signs of leakage, such as wet spots, color changes, or residue on the casing.
Smell test
Smell for any abnormal chemical odor around the battery.
A leaking lithium battery may release a noticeable irritating odor, which is a signal of leakage.
Check the contact points
Check for corrosion or abnormal substances on the contacts or terminals of the battery, as leaks may form corrosive substances at the battery connections.
Abnormal use of equipment
If devices powered by lithium batteries experience abnormal or unstable operation, it may be a sign of battery leakage affecting their performance.
Battery performance monitoring
Pay attention to the performance changes of the battery. If the battery life is significantly shortened or the power consumption rate is abnormally fast, it may be due to leakage affecting the battery capacity.
Leakage of lithium batteries is not common under normal use. But if you suspect that the lithium battery may leak based on the above inspection, it is necessary to take appropriate safety precautions and handle the battery with caution.
Methods for instrument detection for leakage:
①Helium detection method
Inject helium gas into the lithium battery and then use a mass spectrometer to detect the helium gas.
If the mass spectrometer can detect the presence of helium, it usually means that there is a leakage problem with the battery.
②Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) Detection
Detecting the concentration of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during lithium battery leakage through photoionization sensors (PID).
VOC detection can detect small leakage points and locate the leakage source.
③Electrolyte composition analysis
By analyzing the composition and concentration changes of the electrolyte, it is possible to determine whether a lithium battery is leaking.
If the electrolyte contains moisture or impurities, it may indicate a battery leak.
④Stress testing method
Place the lithium battery in a sealed container and monitor the pressure changes inside the container. If the battery leaks, the pressure reading will change.
This method requires professional testing equipment to complete.
⑤Temperature monitoring
By monitoring the temperature changes of lithium batteries during charging, it is possible to determine whether the battery is leaking. If the battery temperature rises abnormally, it may indicate a leak.
⑥Ultrasonic testing
Using ultrasonic testing equipment to inspect lithium batteries can detect small leakage points and internal defects.
Once a battery leak is confirmed, please follow the guidelines previously discussed for handling leaked lithium batteries.
If you are unsure how to handle it on your own, it is recommended to seek professional help, and GycxSolar is your loyal helper.
Throughout the entire process, please always prioritize your personal safety.
Part 6. How to clean leaked battery?
Here are some standard handling steps for dealing with severe leakage of lithium batteries. You can learn and refer to this process:
Prioritize ensuring one’s own safety
Ensuring personal safety is the most important thing. If the leaked liquid comes into contact with the skin or eyes, immediately rinse the affected area with plenty of water and seek medical help immediately.
Determine whether there is a leaked battery:
Check the battery box
Check if the battery casing is intact and undamaged. Shell damage may be caused by improper installation, welding slag inside the battery box, or chassis impact.
Evaluating the condition of the casing helps identify potential sources of leakage.
Check the safety valve
Remove the cover plate and inspect the safety valve for any signs of electrolyte leakage. Ensure that the valve is in the open position and check if the electrolyte is flowing into the battery.
This helps to determine if there is a leak in the safety valve.
Test sealing performance
If no abnormalities are found in the first two steps, the integrity of the seal needs to be evaluated.
Pressurize and inflate the battery in water, and observe for any bubbles. The appearance of bubbles indicates that there is a problem with the seal, while the absence of bubbles indicates that the seal is intact.
Remove electrolyte during charging
Charge the battery and check for electrolyte leakage.
If electrolyte is found, please remove it carefully to prevent further leakage.
Attention: If it has been previously determined that the battery is leaking, do not proceed with this step. This is extremely dangerous. Please refer directly to the handling measures.
Cleaning and repairing leakage sources:
Prevent leakage and spread
Use appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, to prevent further harm from leaks.
Isolation and ventilation
Under confirmed safety conditions, move the leaked lithium battery to a safe area and keep it away from flammable and other hazardous materials.
Ensure good ventilation in the area to prevent the accumulation of harmful gases.
Clean up leaks
For small-scale lithium battery leaks, suitable absorbent materials such as dry gypsum or specialized absorbents can be used for cleaning.
During the cleaning process, use appropriate tools to avoid direct contact with the leaked material.
Repair the leakage source
In the step of determining whether there is a leak, if the leak source is identified, the area can be carefully cleaned with a knife.
Then, use a strong battery specific adhesive to firmly seal the leakage point.
Waste disposal
Put the cleaned leaked material and absorbent material into a sealed container for appropriate handling. Comply with local regulatory requirements and ensure that these materials are handled by professional waste disposal agencies.
To reduce the risk of battery leakage, it is recommended that consumers choose genuine high-quality batteries from reputable sources when purchasing batteries.
Timely resolution of battery leakage issues and ensuring appropriate battery quality can reduce potential risks and provide you with a safer battery usage experience.
Emergency measures
If you come into contact with a leaking lithium battery, please follow the following first aid measures:
Skin contact:
Immediately remove any potentially contaminated clothing and rinse the affected area under running water for at least 15 minutes.
Seek medical assistance to ensure proper assessment and treatment.
Contact with eyes:
Rinse the eyes with running water or saline solution for a few minutes.
Seek medical attention immediately for a thorough examination.
Inhalation of smoke and gas:
Move to fresh air as soon as possible to avoid further contact.
Ensure that the respiratory tract is unobstructed. If the patient has difficulty breathing, please provide oxygen.
If the patient stops breathing, immediately perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation and seek medical assistance.
Ingestion:
If accidentally swallowing electrolyte, rinse your mouth with water and then drink milk or egg whites (if available). Don’t induce vomiting.
Seek medical attention immediately for appropriate assessment and care.
These first aid measures are general recommendations. Once in contact with a leaking lithium battery, it is necessary to immediately contact medical professionals to ensure a comprehensive assessment and appropriate treatment.
Part 7. How to prevent battery leakage?

To ensure the safe use and performance of lithium batteries, the following are some measures to prevent leakage:
Choose high-quality batteries
Purchase batteries from reputable brands known for their strict quality control and safety standards.
Check the expiration date of the battery and avoid using expired batteries as they are more prone to leakage.
Properly store batteries
Store the battery in a cool and dry place, avoiding direct sunlight and extreme temperatures to prevent battery expansion, rupture, or leakage.
Stay away from humid environments as water may react with chemicals inside the battery, causing leaks.
Store batteries in an orderly manner, using original packaging or specialized battery storage boxes to prevent contact with conductive materials.
Avoid overcharging and deep discharging
Use a charger compatible with the battery type to prevent overcharging.
Monitor the charging process to avoid prolonged charging.
Avoid completely discharging the battery to prevent instability and potential leakage risks.
Be careful to protect the battery
Avoid puncturing, squeezing, or dropping the battery to prevent damage to the battery casing.
After handling batteries, especially leaking batteries, be sure to wash your hands and avoid contact with chemicals.
Regularly check the battery
Regularly check the battery for damage or deformation, signs of corrosion, expansion, or leakage.
Abnormal behavior or performance degradation of monitoring devices may be signs of battery issues.
And replace the old batteries that have been stored in unused devices for a long time.
Properly dispose of batteries
Dispose of batteries in accordance with local regulations to avoid environmental pollution.
Utilize battery recycling programs to ensure safe and responsible disposal of batteries.
Use battery box or battery holder
Store batteries separately using insulated, original packaging, or battery boxes and holders designed for safe storage.
Prevent contact with conductive materials.
Stay away from metal objects that may cause short circuits.
Avoid mixing battery types
Do not mix different types of batteries in the same device.
Mixing alkaline batteries with lithium batteries or rechargeable batteries with non rechargeable batteries to avoid leakage and malfunction.
Avoid exposure to extreme conditions
Avoid exposing the battery to extremely cold or hot environments. Stay away from direct sunlight, extreme temperatures, and humidity.
Use a dehumidifier to control the humidity in the battery storage area.
Taking these preventive measures can effectively reduce the risk of lithium battery leakage and ensure the safe use of the battery.
Although these preventive measures help reduce the risk of lithium battery leakage, it is crucial to remain vigilant and always prioritize safety.
If you suspect a battery leak or encounter any issues related to lithium batteries, the safest approach is to seek professional help or contact the manufacturer for guidance.
At the same time, when purchasing lithium batteries, choose reputable manufacturers and suppliers to ensure battery quality and safety standards.
Devices with built-in protection circuits, such as GycxSolar’s LiFePO4 lithium batteries, are equipped with BMS (Battery Management System) to ensure safe use.
Conclusion
Lithium batteries usually have leak proof designs, but some factors may still cause leaks.
Poor quality manufacturing, improper use, and short circuit risk are the main causes.
Users can reduce the risk of lithium battery leakage and ensure the safe operation of equipment by understanding these factors and taking appropriate safety measures.
Please remember that purchasing batteries from reliable sources, handling them responsibly, and implementing safety measures are crucial for preventing lithium battery leaks and maintaining overall battery safety.
Choosing GycxSolar eliminates the need to pay attention to the entire process of purchasing, testing, and after-sales service.
