As solar panels and other electrical systems enter People’s Daily life, people are paying more and more attention to how to improve the power supply efficiency and performance of these devices. Improving energy transmission efficiency can not only increase power supply, but also reduce cost waste. Apparent power and effective power are two important concepts when discussing energy transmission efficiency.

In this article, we will show you the kilovolt-ampere (kVA), the unit of measurement of apparent power, and how to convert amps kva.
What is the ampere (A)?
The ampere is a unit of current (I) used to measure current and represents the flow of charge through a conductor. From a microscopic point of view, it indicates how much charge passes through a certain section of the circuit at a moment, that is, how fast the current passes through a certain section.

What is kilovolt-ampere (KVA)?
Kilovolt-ampere is a measure of power, essentially the product of kilovolts and amperes. The volt-ampere (VA) is also a unit of power, and the conversion relationship between the two is:
1KVA = 1000VA
It needs to be clear that the difference between kilovolt-ampere and other power units is the efficiency difference when the electrical energy is transmitted in the circuit, resulting in the difference between effective power and apparent power, which also leads to the difference between kilovolt-ampere and watt and other power units.
What is the difference between kVA and other power units?
Although kilovolt-ampere and watt are both units of power, there are obvious differences between them. Kva is usually used to describe the apparent power (S) in a circuit, which is calculated as the product of the AC voltage and current in the circuit, reflecting the potential power capacity of the circuit.
The watt is a measure of effective power, representing the actual power present in the circuit. When the current and voltage in the circuit are consistent, the apparent power is equal to the effective power, and as the consistency between the current and voltage is reduced, the difference between the two becomes larger, and the effective power transmitted in the circuit is reduced, but under normal circumstances, the effective power is usually not reduced to zero.
How to convert Amps to kVA?
After understanding the physical units of amperes and KVA, we can learn how to convert amps to kva. It should be known that amperes and kilovolt-ampere do not belong to the same unit of measurement of physical quantities, in order to achieve the conversion between the two, we need to introduce an intermediate unit of measurement of physical quantities: volts (v).
The conversion formula is as follows:
S (KVA) = I (A) x {V (v) ÷ 1000}
In the formula, S is the apparent power, I is the circuit current and V is the circuit voltage. Dividing by 1000 in the formula is to convert volts to kilovolts so that the units match.
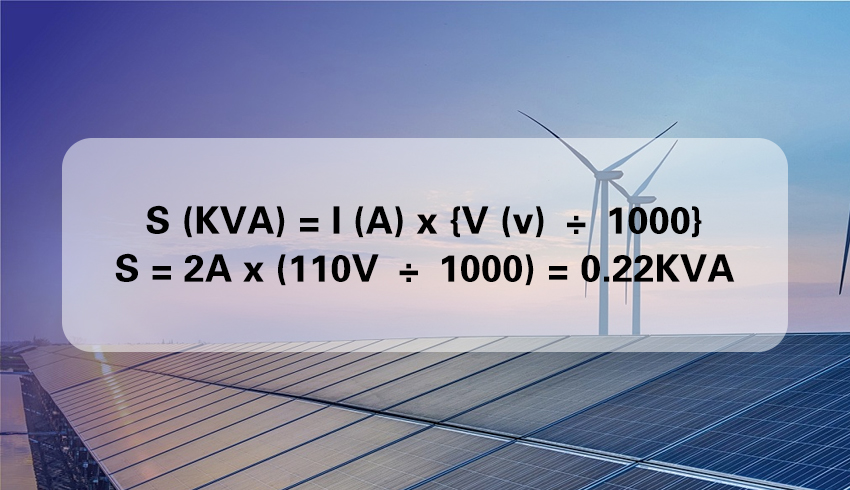
Give an example
In order to let you better grasp the above formula, we will take the household circuit as an example to calculate. Assuming that the voltage of the circuit is 110v and the current is 2A, the apparent power S = 2A x (110V ÷ 1000) = 0.22KVA.
By this example, you should have mastered the above formula. In fact, for commonly used circuits, it is divided into two types, one is DC, and the other is AC. The above formula is generally only used when calculating DC, and for AC, we need to use a more complex conversion formula. Specifically, AC circuits can be subdivided into single-phase AC and three-phase AC.
single phase alternating current
First of all, we need to understand what is single-phase AC, and single-phase AC refers to a type of circuit in which there is only a single AC voltage. In this circuit, the current and voltage are constantly changing over time at a specific frequency.
For single-phase AC circuits, the formula for converting amperes to KVA is as follows:
S (KVA) = I (A) x {V (v) ÷ 1000}
It is worth noting that the V in the formula represents the effective value (RMS) voltage in an AC circuit, that is, the ratio of the DC voltage of the circuit to the DC voltage that can produce the same heating effect. This is used because the voltage in an AC circuit changes over time, so the effective value of the voltage needs to be used in the calculation.
three-phase alternating current
Three-phase alternating current (AC), which is the most commonly used circuit type in practical applications, is composed of three identical frequencies, the same potential amplitude, and the phase between them is 120° apart.
In a three-phase AC circuit, the formula for converting amperes to KVA is calculated in two different ways:
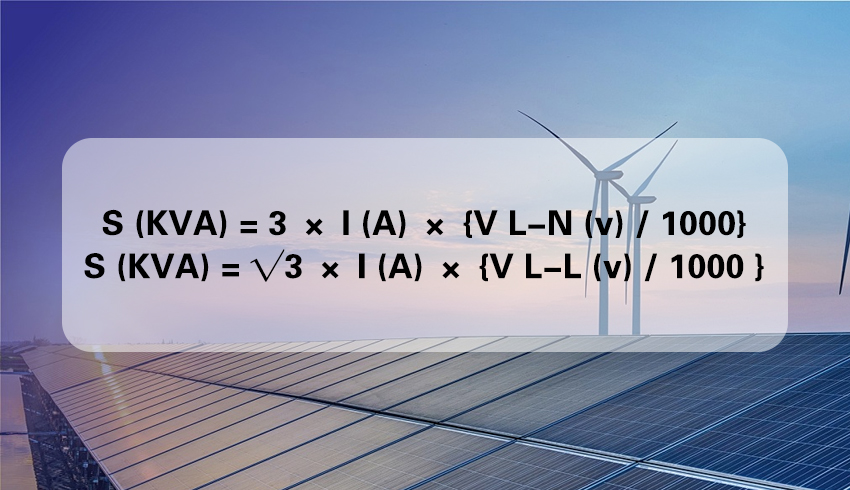
The first is to convert the RMS voltage into line voltage (V LN) for calculation, and the conversion formula is as follows:
S (KVA) = 3 × I (A) × {V L-N (v) / 1000}
The other is to convert the RMS voltage into inter-line voltage (V LL) for calculation, and the conversion formula is as follows:
S(KVA) = √3 × I(A) × {V LL(v) / 1000 }
Table of Amps to kVA Convert
Below is a table showing the conversion of various ampere-to-kilovolt-ampere (kVA) values, with the data in the table arranged in order of the ampere-value from smallest to largest. In the conversion calculation, we set the voltage to 240V and the power factor to 0.8 to show the corresponding conversion results.
| Amps (A) | Voltage (V) | Power Factor (PF) | kVA |
| 20 | 240 | 0.8 | 6.00 |
| 50 | 240 | 0.8 | 15.00 |
| 100 | 240 | 0.8 | 30.00 |
| 200 | 240 | 0.8 | 60.00 |
| 300 | 240 | 0.8 | 90.00 |
| 400 | 240 | 0.8 | 120.00 |
| 600 | 240 | 0.8 | 180.00 |
| 1200 | 240 | 0.8 | 360.00 |
Convert 10 Amps to kVA
To convert 10 amps to kVA at 240V with a power factor of 0.8:
kVA=10×240/1000×0.8=3 kVA
Convert 100 Amps to kVA
To convert 100 amps to kVA at 240V with a power factor of 0.8:
kVA=100×240/1000×0.8=30 kVA
Frequently Asked Questions
How many Amps is 1kVA?
1000 volt Amps is equal to 1kVA
How much is 30 amps to kVA?
When the electrical equipment drawing 30Amps at 220V Ac then the Apparent power will be 6.60 kVA.
