How to determine the efficiency of solar panels?

Table of Contents
1. Introduction: The Rise of Renewable Energy
The global drive toward clean and sustainable energy has led to a rapid increase in the use of solar energy. As climate change concerns grow and fossil fuel reserves dwindle, solar power is emerging as one of the most viable and eco-friendly energy sources. But how exactly does a solar panel convert sunlight into electricity? Understanding this process not only demystifies the technology but also highlights its potential for reducing energy costs and carbon footprints.
In today’s competitive renewable energy market, consumers and professionals alike are increasingly interested in understanding the inner workings of solar technology. Whether you are a homeowner looking to reduce your energy bills or an industry professional exploring renewable energy solutions, learning how this technology works is essential. In this article, we’ll break down the conversion process into clear, digestible parts, supported by authoritative sources.
For additional detailed insights, visit our dedicated section on Solar Panels.

2.Understanding Photovoltaic Panels: The Science Behind Solar Energy
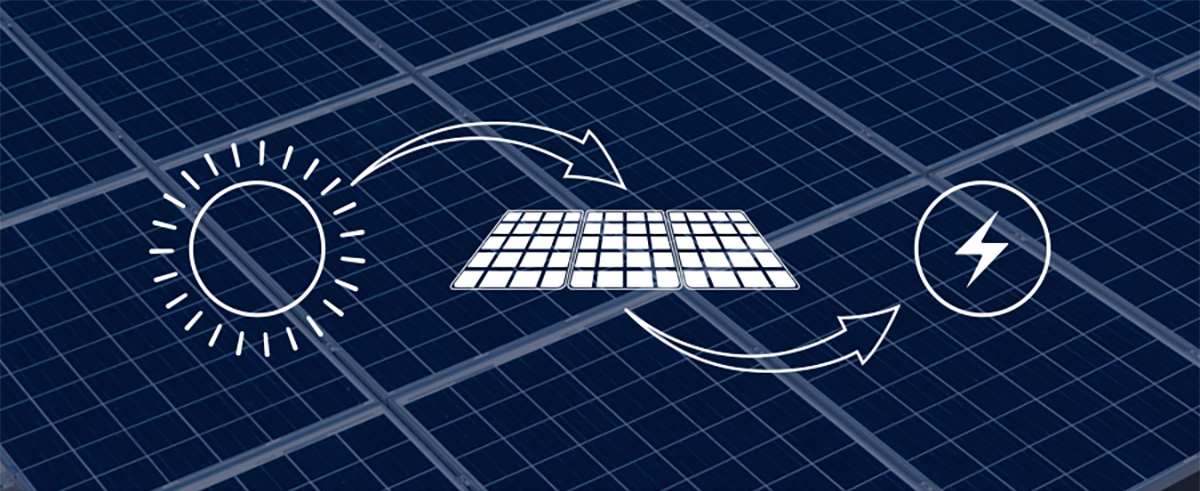
At the heart of every solar energy system is the photovoltaic panel, a device that directly converts sunlight into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect. This phenomenon, discovered in the 19th century, is the underlying principle behind solar electricity generation.
The Photovoltaic Effect
When sunlight strikes the surface of a photovoltaic panel, its energy is absorbed by semiconductor materials—most commonly silicon. The absorbed light energy knocks electrons loose from their atoms, generating a flow of electric charge. This process occurs at the microscopic level in the PV cells contained within the panel. The generation of electron flow, or current, is the first step in turning solar energy into a usable electrical output.
For a detailed scientific explanation of the photovoltaic effect, you can review the information available on the related sites.
Variants and Terminology
In industry discussions, photovoltaic panels are often referred to by several names, such as “PV panels” or “solar cells.” These terms are interchangeable but emphasize different aspects of the technology:
- Photovoltaic Panels: Focuses on the light-to-electricity conversion.
- PV Systems: Broad term including panels, wiring, and inverters.
- Solar Cells: The individual units that make up the panels.
The science behind these panels is both elegant and complex, with ongoing research aiming to boost efficiency and reduce production costs.
3. Components of a Solar Energy Module: Building Blocks of a Solar System
A solar energy module comprises several layers and components designed to optimize the conversion of sunlight into electricity. Understanding the module’s structure helps explain how each element contributes to the overall performance of the system.
Layers and Materials
Solar energy modules typically consist of the following components:
- Glass Cover: A layer of tempered glass protects the photovoltaic cells from the environment while allowing maximum light penetration.
- Encapsulant Layers: These transparent layers (usually made of EVA or similar materials) secure the solar cells and provide insulation.
- Solar Cells: The heart of the module, where the photovoltaic effect takes place. These cells are made from crystalline silicon (monocrystalline or polycrystalline), though emerging technologies also use thin-film materials.
- Backsheet: A protective layer at the rear of the module, usually made from a durable polymer, which shields the internal components from moisture and physical damage.
- Frame: An aluminum frame that supports the module and facilitates its mounting on roofs or other structures.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the module’s durability, efficiency, and overall cost-effectiveness.
Manufacturing Innovations
Manufacturers continuously refine module designs to enhance light absorption, reduce energy losses, and extend the lifespan of the panels. Innovations in materials science and cell design have led to higher efficiency rates. For example, advancements in anti-reflective coatings and bifacial cell technologies are driving improvements in energy yield.

4. Inside a PV System: The Role of Inverters and Wiring
Beyond the solar energy module, a complete PV system includes several critical components that transform the direct current (DC) generated by the panels into alternating current (AC) used by household appliances and the grid.
The Inverter
One of the most essential components of a PV system is the inverter. Solar panels produce DC electricity, which is not directly compatible with the AC power used in most homes. The inverter’s function is to convert this DC power into AC power, making it usable for everyday electrical appliances. There are different types of inverters available, including string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers, each with its own set of advantages.
- String Inverters: Commonly used in residential installations, where multiple panels are connected in series.
- Microinverters: Attached to each panel, allowing for individual performance monitoring and optimization.
- Power Optimizers: Often used in conjunction with a central inverter, these devices maximize the output of each panel by mitigating issues such as shading.
The selection of an inverter can affect the overall efficiency and cost of the solar energy system.
Wiring and System Integration
After the inverter, proper wiring is crucial to ensure that the converted AC electricity reaches your home’s electrical system safely and efficiently. A well-designed wiring system minimizes energy losses and helps maintain the system’s performance over time. Additionally, modern PV systems often include monitoring solutions that allow users to track energy production and consumption in real time.
5. Efficiency of solar panels: Maintenance and Environmental Considerations
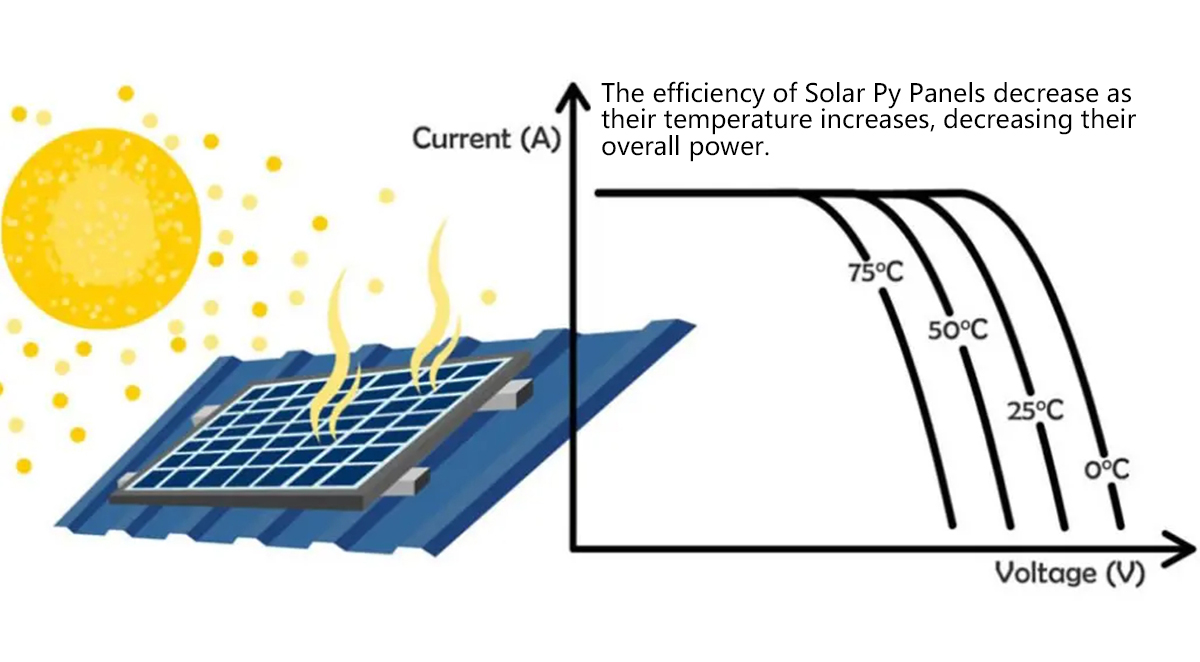
The efficiency of any solar installation is influenced by several external and internal factors. In this section, we discuss maintenance practices, environmental impacts, and strategies to maximize energy output.
Routine Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to ensure that Solar Panels operate at peak efficiency. Dust, bird droppings, and debris can accumulate on the surface of the panels, reducing the amount of sunlight that reaches the photovoltaic cells. In many cases, natural rainfall can help clean the panels, but in drier or dustier environments, periodic manual cleaning is advisable.
GycxSolar provide professional maintenance services and smart monitoring systems can alert owners to performance issues, helping to identify when cleaning or repairs are needed.
Environmental Factors
Several environmental factors influence the efficiency of solar panels:
- Sunlight Exposure: The amount of sunlight a panel receives directly affects its output. Shading from nearby trees, buildings, or other obstructions can significantly reduce performance.
- Temperature: While solar panels are designed to operate under various conditions, extreme heat can decrease their efficiency. Many modern panels incorporate temperature management systems to mitigate these effects.
- Orientation and Tilt: The angle at which panels are installed can impact energy generation. Ideally, panels should face true south (in the northern hemisphere) or true north (in the southern hemisphere) to capture maximum sunlight.
Advanced Optimization Techniques
Innovations such as solar trackers—which adjust the panels’ angle throughout the day—can enhance energy production by keeping the panels aligned with the sun’s path. Additionally, integrating battery storage systems allows homeowners to store excess energy during peak sunlight hours for later use, further increasing the overall system efficiency.
6. Environmental Impact and Performance of Renewable Energy Panels
Solar energy is widely recognized as a clean, renewable resource that contributes significantly to reducing carbon emissions. The impact of renewable energy panels extends beyond individual energy savings, influencing broader environmental and economic trends.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
One of the most compelling advantages of solar energy is its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By generating electricity without burning fossil fuels, solar panels help lower overall carbon dioxide output. Studies have shown that a typical residential solar installation can offset several tonnes of CO₂ per year. This reduction in emissions not only contributes to global climate goals but also supports local efforts to improve air quality.
For more detailed data on carbon savings and environmental benefits, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) provides extensive research and reports.
Lifecycle and Sustainability
The production and disposal of solar panels involve environmental considerations as well. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices in the production process, such as using recycled materials and reducing energy consumption during manufacturing. End-of-life recycling programs are also becoming more common, ensuring that solar panels have a lower environmental impact over their entire lifecycle.
Economic analyses have also shown that while the initial production of solar panels does have an environmental cost, the long-term benefits—both in terms of energy savings and reduced emissions—far outweigh these concerns.
7. The Future of Solar Electric Panels: Innovation and Trends
The solar energy industry continues to evolve, driven by both technological advancements and shifting economic landscapes. Solar panels are at the forefront of this innovation, with new breakthroughs promising even higher efficiencies and broader applications.
Emerging Technologies
Recent developments in solar technology include:
- Bifacial Panels: These panels capture sunlight on both sides, leading to increased energy output in certain installation scenarios.
- Perovskite Solar Cells: With the potential for even higher efficiencies at lower costs, perovskite technology is rapidly advancing, although it still faces challenges related to long-term durability.
- Integrated Solar Solutions: Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) are being designed to blend seamlessly into building materials, transforming rooftops and facades into energy-generating surfaces.
Innovations like these are expected to further reduce the cost of solar installations while increasing energy yield, making solar power more accessible worldwide. For more on future trends, the International Energy Agency (IEA) offers up-to-date insights into global solar trends.
Market and Policy Developments
Government policies and market incentives play a crucial role in shaping the future of solar energy. Many countries now offer subsidies, tax incentives, and favorable financing options to promote solar adoption. These measures are helping to drive down the cost of solar installations and accelerate the shift toward renewable energy.
The continuous growth of the solar market is supported by a robust supply chain and increasing consumer awareness. Analysts predict that as efficiencies improve and costs continue to fall, solar energy could become one of the most cost-effective sources of electricity in the near future.
8. Conclusion
Solar panels represent one of the most promising technologies for harnessing renewable energy. From the fascinating science of the photovoltaic effect to the intricate components of solar energy modules, every aspect of the technology is designed to maximize the conversion of sunlight into electricity. By understanding how these systems work—from the basic function of solar cells to the advanced roles of inverters and optimizers—we can appreciate the profound impact they have on reducing energy costs and mitigating environmental harm.
The journey of solar energy conversion involves sophisticated technology, continuous innovation, and thoughtful integration into our daily lives. With ongoing research and development, the efficiency and sustainability of solar panels will only improve, paving the way for a greener and more energy-independent future.
As you explore the world of renewable energy, it is important to consider factors such as installation orientation, environmental conditions, and maintenance practices. These elements not only influence performance but also contribute to the long-term reliability of the system.
In summary, the conversion of sunlight into electricity is a remarkable interplay of science and technology. By embracing solar energy, we are not only investing in a cleaner future but also reaping tangible benefits in terms of energy savings and environmental stewardship.
