In the rapid development of science and technology, the battery is the energy core of many devices, and its performance is related to the operation of equipment. As a key indicator of battery performance, ampere hours is of great significance. It shows exactly how much power the battery has and how long it lasts.
So, this article takes you to understand the battery ampere hours, and how to calculate and significance, let’s take a look.
What is ampere hour?
Ampere hours is an important unit used to measure battery capacity, which clearly indicates the rated power that the battery can output in an hour.
Specifically, take a battery labeled 50Ah as an example, which means that the battery can continuously and steadily output 5A current for a period of 10 hours. From the point of view of electrical principles, the higher the value of the ampere hours, it means that in the same unit time, more electrons inside the conductor can pass smoothly, and the directional movement of electrons forms a current, so it means that the current generated at this time will be larger.
In this way, ampere-hours become a key indicator for us to understand and evaluate battery performance, helping us better choose the right battery according to actual needs.
How to calculate the ampere hours of the battery?
Normally, the surface of the battery is clearly marked with its ampere hours number, which represents the maximum current capacity that the battery can discharge continuously under normal operating conditions. However, if the battery is not marked with this value, or if you want to calculate it yourself, you need to take a certain method to get the result.
First, we need to accurately determine the battery’s current flow and discharge duration. A multimeter is a common tool that can be used to measure the battery’s current flow. In electrical terms, a current of 1A means that at some point in the circuit, a charge of 1C will pass through every unit of time. After accurately measuring the current value, we also need to record the discharge time of the battery.
Next, you can use the formula to calculate. The calculation formula is: ampere-hour (Ah) = current flow (A) x discharge length (h). For example, if a battery is discharged at a steady current of 20A and continues to discharge for 5 hours, the number of ampere-hours of this battery is 20A×5h = 100Ah.
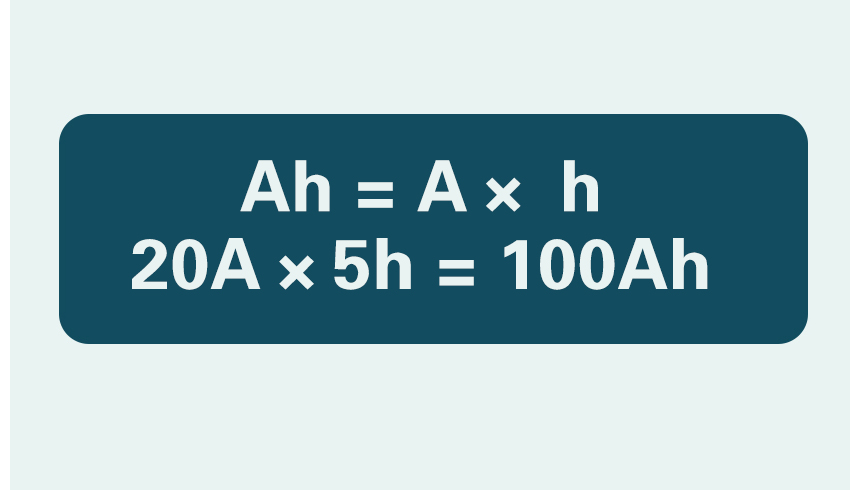
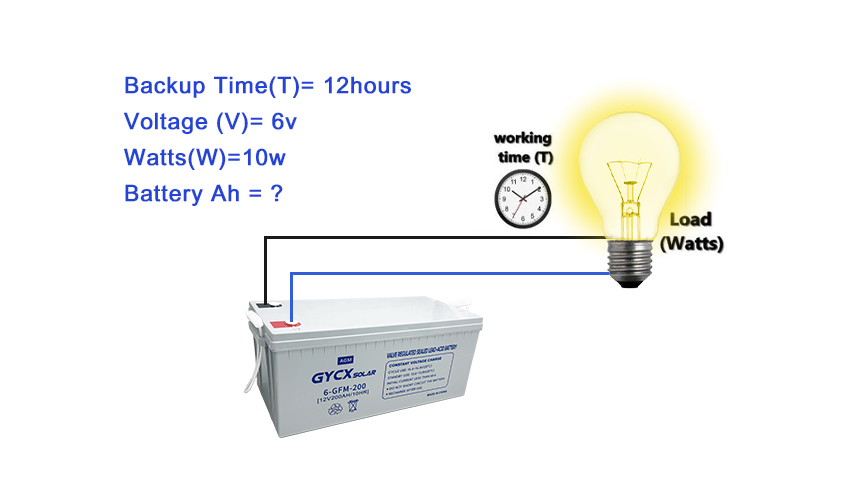
In addition, there is another way to calculate. When we know the watt-hour (Wh) value of the battery, combined with the battery voltage (V), we can also calculate the number of ampere-hours of the battery. The corresponding formula is: ampere-hour (Ah) = watt-hour (Wh) ÷ battery voltage (V). For example, for a battery labeled 600Wh, 12V, its ampere-hour number is 600Wh÷12V = 50Ah. Through these methods, we can calculate the ampere-hour number of the battery more accurately, in order to better understand the performance and capacity of the battery.
Unit conversion and common battery ampere hours
In the conversion of battery capacity units, there is such a quantitative relationship: 1Ah=1000mAh. This conversion between units can help us more flexibly represent battery capacity under different accuracy requirements.
In terms of common battery types, deep-cycle batteries are widely used for their ability to withstand multiple deep charge and discharge cycles, and their capacities are mostly 100Ah and 200Ah. Lithium batteries, with the advantages of high energy density and long life, stand out in many fields, in general, the capacity of lithium batteries is more than 300Ah.
However, in the actual selection of batteries, you can not only make decisions based on common capacity values, but you need to fully consider the equipment used. If the selected battery capacity is too small, it may not be able to meet the power demand of the device, resulting in a power outage, so that the device is forced to stop running. Therefore, a reasonable choice of battery capacity is crucial to ensure the stable operation of the equipment.
What does a high battery Ah mean?
Some people may think that the higher the ampere-hours of the battery, the higher the discharge, but in fact, the ampere hours of the battery is not proportional to the discharge, and the ampere-hours of the battery is also closely related to its use time.
When the ampere-hour (Ah) value of the battery is higher, it indicates that the battery has a stronger power supply capacity. On the one hand, it can continue to provide stable power for some devices for a long time, ensuring the normal operation of the device for a long time, without frequent battery replacement or charging.
On the other hand, in a short period of time, a battery with a high Ah value can also provide more power to meet the power needs of the equipment during instantaneous high-power operation. Not only that, it can reduce the work burden of some components of the battery to a certain extent, helping to extend the overall service life and performance of the battery
Factors affecting the battery ampere-hour size
Battery charge and discharge current: When using the battery, the battery charge and discharge current for a long time will affect the active substance on the battery plate, resulting in a reduction in the capacity of the battery and too short the service life of the battery. More seriously, this situation will also greatly shorten the service life of the battery, so that it can not be stable for a long time to power the device.
Ambient temperature: At higher temperatures, the chemical reaction inside the battery will intensify, generate more energy, and the battery capacity will increase. However, when the temperature is low, the chemical reaction inside the battery will slow down, the battery capacity will decrease, and its power supply ability will also be weakened.
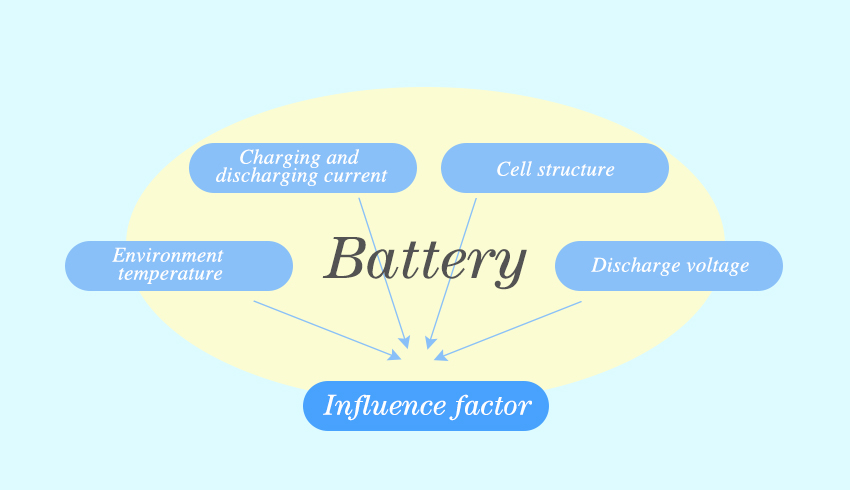
Battery structure: The structural composition of the battery, such as the structure of the plate and the concentration of the electrolyte, will directly act on the chemical reaction inside the battery. Different plate structures and electrolyte concentrations can change the way and speed of chemical reactions, which in turn affects the battery capacity.
Discharge voltage: When the battery is discharged to a certain voltage, there will be a drop in voltage, which will greatly reduce the capacity of the battery in the long term, so it is necessary to determine a termination voltage to avoid this damage.
Calculate the ampere-hours of the battery pack
A battery pack or battery pack is a series of individual cells connected together. They can be connected in series or parallel and are commonly used to store energy produced by solar systems. By connecting multiple cells together, you can increase the amperage and voltage of the combined battery pack to meet your power needs. In addition, battery packs are generally more cost-effective than other methods of power storage.
So how do you calculate the ampere-hours of a battery pack, rather than the ampere-hours of a single cell? In fact, the basic formula used here is not complicated. When the batteries are connected in parallel, the ampere hours of the battery pack can be obtained by simply adding the ampere-hours of each cell. For example, there are two 12V, 50Ah batteries:
When two 50Ah batteries are connected in parallel: 50Ah + 50Ah = 100Ah
When the battery is connected in series and we want to know the voltage of the battery pack, it can be calculated by a simple addition operation. For example, for two 12V, 50Ah batteries, connect them in series, add the voltage of different batteries, you can get the total voltage of the battery pack:
When two 12V (50Ah) batteries are connected in series: 12 volts + 12 volts = 24 volts
When do watt-hour and ampere-hour calculations need to be performed?
The main reason for these calculations is to know exactly what the battery’s energy capacity is. When we intend to use batteries to power a device, it is critical to know the battery capacity required to run the device.
In the process of designing solar installations, conversion between watts and ampere hours is often required. Specifically, we first determine the number of watts of each device in a day and add them together to get the total number of watts of electricity in a day. This total wattage is then divided by the voltage of the device to give the corresponding number of ampere-hours.
This calculated number of ampere hours is significant and will determine the number and type of batteries you need, the size of the solar panels you need, and even the thickness of the wiring.
Conclusion
In summary, the ampere-hour of the battery is a value that reflects the capacity of the battery, and you should choose the right capacity battery for your device so that it runs better.
To learn more about how lithium battery systems can power your lifestyle, check out Gycx Solar, where our sales and customer service team is here to help!
