In the assembly process of lithium-ion battery cells, there are mainly two techniques: winding and Stacking. The establishment of these two technologies is closely related to the following key technical points: space utilization, cycle life, manufacturing efficiency, and manufacturing investment of battery cells.
Lithium ion batteries can be divided into soft pack, square, and cylindrical batteries according to their packaging methods and shapes. From the perspective of internal molding process, soft packs and square batteries can be wound or laminated. However, cylindrical batteries can only be wound due to their curvature everywhere.
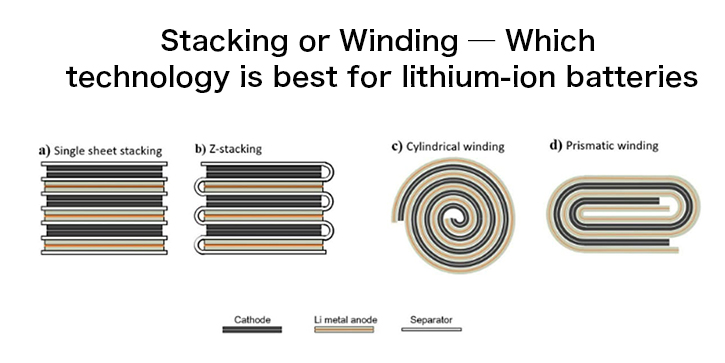
Among these two technologies, the winding process has a longer development time and has the advantages of mature technology, low cost, and high yield. But with the development of electric vehicle technology, the stacking process has gradually become a rising star due to its high volume utilization rate, stable structure, low internal resistance, and long cycle life, and stands out in comparison with the winding process. Although the lamination process may require higher initial investment costs in some aspects, its long-term performance advantages and efficiency improvements make it an important development direction for future battery manufacturing technology.
What is winding technology?

The winding process involves winding the cut positive electrode sheet, separator, and negative electrode sheet into a predetermined size and shape, similar to a battery jelly roll. This process uses a specific winding machine to sequentially wind and compact the material through a winding needle, forming cylindrical or square battery cells. Subsequently, these battery cells were placed in corresponding metal shells to complete the initial construction of the battery.
The design capacity of the battery cell determines the size of the slitting coil and the parameters of the winding coil.
What is stacked battery technology?

Stacked battery tech is the process of cutting positive and negative electrode sheets to specific sizes according to design requirements, and then stacking the cut positive electrode sheet, separator, and negative electrode sheet in sequence to form a multi-layer structure. This structure is subsequently divided into multiple small battery cells, which are ultimately stacked and assembled into complete individual cells through welding and packaging processes.
This method can improve the space utilization of the battery and optimize its overall performance.
Comparing process of stacking battery vs winding
| Stacking | Winding | |
| Energy density | High. There is a higher utilization rate of space. | Lower. Due to the influence of shape and angle, the larger the space, the lower the utilization rate. |
| Structural stability | Higher. The internal structure is stable, and the reaction rate is relatively low. | Lower. The internal charging and discharging reaction rate is uneven. |
| Security | High security. The stress distribution is more consistent. | Lower. Potential issues that may affect the quality of use, such as powder loss, pole expansion, and diaphragm stretching, are prone to occur at the bending point. |
| Process maturity | Low. There are a large number of polarizer pieces, and the initial investment cost of the equipment is high. | High. Mature technology and low investment cost. |
| Cycle life | Longer. Low internal resistance, high stability of battery chemical system, and long service life. | Shorter. It is prone to deformation in the later stages of use, which affects the battery’s cycle life. |
| Fast charging adaptation | Easy to adapt. Multi pole parallel connection, low internal resistance, can complete high current charging and discharging in a short time, and has high battery performance. | Poor adaptability. During the charging and discharging process, the degradation rate of active substances at high temperatures accelerates, resulting in low battery rate performance. |

Different battery types use different manufacturing processes:
Soft pack battery cells: Both technologies are used, depending on the battery cell manufacturer. Stacking technology is often used because its flexible shape is suitable for stacked structures.
Blade cells: Designed and produced using stacking technology.
Square cell: Both stacking and winding processes are available. At present, the market is mainly dominated by the winding process, and the technology is transitioning towards stacking.
Cylindrical battery cell: As a mature product, it has always adopted the winding process.
These process choices reflect a comprehensive consideration between battery design, manufacturing efficiency, and battery performance requirements.
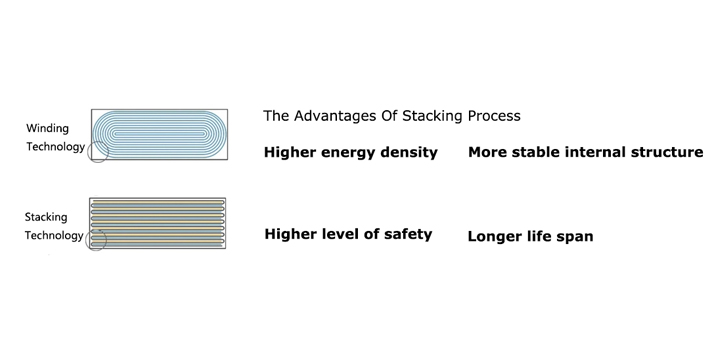
Lithium ion battery cells using stacking technology have advantages over winding technology

Cell stack has higher battery energy density
Lithium ion batteries formed through stacking technology have higher energy density, more stable internal structure, higher safety, and longer lifespan.
The winding process has curved edges and corners, resulting in lower space utilization compared to stack battery. However, stacked lithium battery can fully utilize the corner space of the battery. Therefore, when the cell design volume is the same, the energy density of the cell formed by battery stack is higher.
Compared with wound batteries, the energy density of stacking structures can be increased by about 6%.
More stable internal structure
Compared to wound batteries, there is no problem of uneven internal stress at the corners of the stack battery. During repeated use of the battery, the expansion forces of each layer are similar. So even though the stacking process may expand during battery use, the overall expansion force of each layer is similar, so the exterior of the battery stack can remain flat and the stability inside the battery is also high.
During the use of wound batteries, as lithium ions flow and embed, both the positive and negative electrodes will expand. At the corners of the winding process, the internal stress of the inner and outer layers is not consistent. It will cause wavy deformation of the jelly roll battery. This deformation can lead to a deterioration in battery interface performance, uneven current distribution, and accelerated instability of the internal structure of the battery.
Higher security
The coating material at both ends of the winding is prone to significant bending and deformation, and the bending area is prone to powder loss, burrs, and other phenomena. In severe cases, it can cause internal short circuits in the battery, leading to uncontrolled heat generation.
The electrode plate and diaphragm are prone to uneven stress, resulting in wrinkles. The expansion and contraction of the electrode plate and the stretching of the diaphragm can cause deformation of the battery cell. The stacking battery cell is uniformly stressed and there is no bending problem at both ends. In this way, the stack battery has higher security.
Longer life span
As is well known, when the voltage and time are constant, the larger the resistance, the less heat is generated. The smaller the resistance, the less heat is generated.
The battery stacks has a relatively large number of single pole ears, which is twice as many as that of wound batteries.
The more polar ears there are, the shorter the electronic transmission distance and the lower the resistance. Therefore, the heat generation of the stack battery unit is small. However, wound batteries are prone to deformation, expansion, and other issues, which can affect the performance of the battery.
So compared to wound batteries, stacked lithium batteries have a relatively longer lifespan.
The disadvantages of stack battery compared to wound batteries
High investment cost
The number of laminating machines required for a production line is related to the number of battery cells.
Calculated at a price of 3-3.5 million yuan per unit for a single production line, the initial investment cost is too high. And the technology of wound batteries is mature, and the corresponding price is also relatively low.
Low yield rate
The cutting technology for wound batteries is mature, and each battery cell only needs to be cut once for the positive and negative poles, with relatively low difficulty. So the product qualification rate is also correspondingly high.
Stack battery have dozens of small pieces per cell, each with multiple cutting surfaces, making it difficult to control product quality. So the yield rate of the product is low.
Difficult to control
It’s still a matter of process technology. The wound battery only has two pole pieces, and each battery only needs two spot welds, which is easy to control.
Stacked batteries have a large number of stacked electrodes, which can easily lead to virtual soldering. Because all the pole pieces need to be spot welded onto one welding point for fixation, the operation is difficult.
The winding process controls the speed, tension, etc. of the electrode pieces to wind the cut positive and negative electrodes, as well as the separator and other parts together. This characteristic makes the winding process only capable of producing lithium batteries with regular shapes.
The stacking process of stacking battery is to alternately stack the positive electrode sheet, negative electrode sheet, and separator through a machine to form a stacked battery cell. This process can produce lithium batteries with regular or irregular shapes, with higher flexibility in design and operation.
How to choose a technical route? Stacking or Winding?
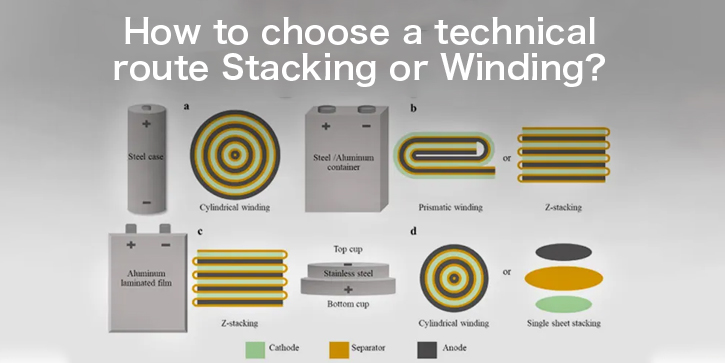
From the perspectives of manufacturing efficiency and yield, stacked growth is the fastest. With the development of stacked battery technology by battery cell manufacturers and the continuous innovation of technology by battery companies, the market is moving towards the direction of designing super stacked + blade battery solutions. It can be considered that this part has the greatest potential.
From the perspective of the technological development direction adopted by different types of batteries, the use of stacking technology for soft pack batteries is becoming a trend and unstoppable.
The standardization of winding process requires improvement in the manufacturing speed of single cell batteries. Square cells will continue to use winding technology without developing in size. But if it is a square shell laminated size, the stacking process should be used.
For consumer batteries, in addition to battery capacity and performance, manufacturers will pay more attention to improving usage efficiency. Therefore, there is a high demand for winding technology.
For power batteries, large modules and large battery cells will be the trend of choice. The stacking process can better leverage its advantages in efficiency, reliability, and other aspects.
The internal resistance of coiled batteries is relatively high, and in order to significantly reduce it, there are high requirements for equipment capability and quality control. This will also increase costs.
The stack battery has a flat battery structure, low internal resistance, and high space utilization efficiency. The top ten lithium battery companies in the world, represented by BYD, all adhere to the stacking route.

If you have any further questions or would like to know which battery is the best choice, please contact us immediately!
Contact GycxSolar immediately to learn more about lithium battery technology!
