When considering solar energy storage devices, people are usually faced with the problem of which type of battery should be selected. The most common choices today are lead acid batteries vs lithium-ion batteries, and to help you decide, this article will compare the characteristics of lithium battery vs lead acid battery and answer some frequently asked questions.

Lithium Battery vs Lead Acid Battery Overview
lithium battery
Lithium-ion batteries are made of lithium metal, in which lithium compounds are used as electrolytes between the positive and negative electrodes. It is commonly used in portable electronic devices, electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
Lead acid battery
Lead-acid batteries are made from lead and are a traditional type of battery in which the electrolyte between the positive and negative electrodes is sulfuric acid. They are widely used in automotive, UPS systems and solar energy applications.
How Do Lead Acid Batteries vs Lithium Ion Batteries Work?
How lithium ion batteries work
Lithium-ion batteries store and release energy by moving lithium ions between positive and negative electrodes. During charging, lithium ions flow from the positive electrode (lithium compound) to the negative electrode (carbon or silicon material). During discharge, lithium ions move from the negative electrode back to the positive electrode. This reaction is achieved by ion conduction in the electrolyte.
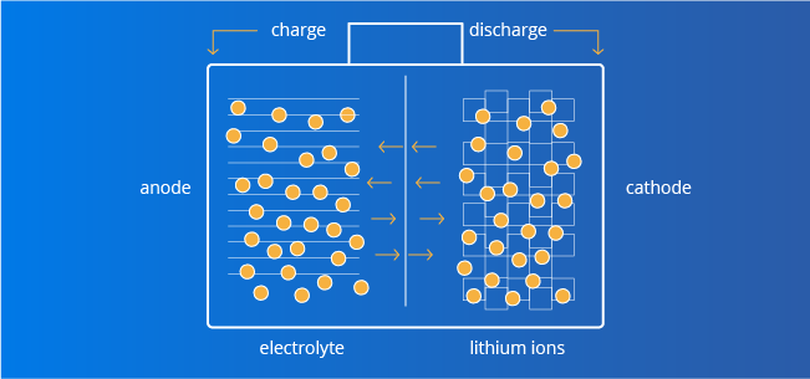
How lead acid batteries work
A lead-acid battery is a battery that stores and releases energy based on a chemical reaction between lead and lead dioxide. During the charging process, an electric current passes through the battery and oxidizes the lead in the lead-acid solution to lead dioxide (positive) and pure lead (negative). During the discharge process, the lead oxide in the lead acid solution reacts with pure lead, releasing electrons and generating an electric current. Lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries use a similar process, but the material is different.
Difference Between Lead Acid Batteries vs Lithium Ion Batteries
The Materials Used
Lead acid and lithium ion batteries work basically the same way, with the difference being the materials used as cathodes, anodes, and electrolytes. Lead-acid batteries use lead as an anode, lead oxide as a cathode, and sulfuric acid as an electrolyte. Lithium-ion batteries use carbon as the anode, lithium oxide as the cathode, and lithium salt as the electrolyte.
Lifespan
Battery life refers to the number of charge and discharge cycles a battery can make without affecting its performance. The cycle life of lithium-ion batteries is usually 5000 times, and full discharge does not affect the cycle life. Lead-acid batteries can last 300 to 500 cycles, and full discharge will affect their life cycle. So over the lifetime of both, lithium-ion batteries are more cost-effective.
Cost
Lead-acid batteries generally have a lower purchase price and installation cost compared to lithium-ion batteries. But lithium-ion batteries last longer than lead-acid batteries, so lead-acid batteries are only more cost-effective than lithium-ion in short-term applications, and lithium-ion batteries are generally a more favorable choice.
Battery Capacity
Battery capacity refers to the amount of energy stored in a battery per unit volume, and while capacity figures vary by battery model and manufacturer, lithium-ion battery technology has been well documented to have significantly higher energy density than lead-acid batteries.
Typical lithium-ion batteries range in capacity from a few hundred mAh to a few thousand mAh, and typical lead-acid batteries typically range in capacity from tens of amps (Ah) to hundreds of amps (Ah). As a result, lithium-ion batteries typically have a higher battery capacity and are able to store more energy in the same size battery, which makes them more advantageous in applications that require high energy density.
Depth of Discharge (DOD)
A battery’s depth of discharge indicates the percentage of batteries that can safely exhaust energy without damaging the battery, typical lithium-ion batteries can safely discharge to 80 to 90 percent of their rated capacity, while lead-acid batteries are recommended to limit discharge to about 50 percent of their rated capacity to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
As a result, lithium-ion has a wider range of discharge depths than lead-acid batteries, which means you can use lithium-ion batteries longer and without recharging, and modern lithium-ion batteries manufactured today are more efficient, with DOD 100%.
Efficiency
Efficiency is a key point of comparison when considering lithium-ion batteries versus lead-acid batteries, with more efficient batteries charging faster, and similar to the depth of discharge, an increase in efficiency means that the effective capacity of the battery is higher.
Most lithium-ion batteries have an efficiency of 95% or higher, due to the high internal resistance, lead acid batteries will produce a certain amount of heat and energy loss during charging and discharging, and the efficiency of lead acid batteries is about 80-85%.
Energy Density
Energy density = (nominal battery voltage (V) x rated battery capacity (Ah)) ÷ battery weight
Lithium-ion batteries typically have a higher energy density and are therefore able to store more energy for the same volume or weight.
Lead-acid batteries typically have a lower energy density, so they store less energy for the same volume or weight and may require more space and weight to achieve the same power output.
Durability
The durability of a battery depends on how long it can last. Lead-acid batteries can last up to 2 years if properly maintained, that is, charged after 50% use, and only 350 cycles or one year if completely emptied or more than 80%. Lead-acid batteries have a higher self-discharge rate, so they may lose their charge when stored for a long time and need to be recharged periodically to maintain their performance.
Lithium-ion batteries are guaranteed for 10 years and last 10,000 cycles. Lithium-ion batteries typically have less self-discharge rate, so when stored for a long time, they can remain charged for a longer period of time without the need for frequent recharge.
Charging Time
Lithium-ion batteries can charge eight times faster than lead-acid batteries. Under the same capacity conditions, if the lead-acid battery takes more than 10 hours to charge, then the lithium-ion battery may be charged in less than three hours.
Safety
Whether it is a lead-acid battery or a lithium-ion battery, overcharging can cause an explosion. The sulfuric acid in lead-acid batteries is highly corrosive and has the potential for leakage, which can produce hydrogen and oxygen if overcharged, leading to an explosion. In lithium-ion batteries, the potential for thermal runaway is high. Thermal runaway is a condition that occurs when the heat generated inside a battery exceeds the heat emitted to the surrounding environment, potentially triggering a battery explosion.
Therefore, whether it is a lithium-ion battery or a lead-acid battery, it requires proper handling, installation and maintenance to ensure safe operation.
When choosing between lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries, specific safety requirements and risk mitigation strategies should be considered to meet the needs of the intended application scenario.
Application
Lithium-ion battery application
- Mobile devices: Lithium batteries are widely used in the mobile device market, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops and portable audio devices, because they are lightweight, efficient and have a high energy density.
- Electric vehicles: Vehicles such as electric cars, electric bicycles and electric scooters have adopted lithium batteries as their main power source because of their high energy density, long life and fast charging characteristics.
- Home electronics: Home electronics, such as drones, smart home devices, and portable power supplies, have also widely adopted lithium battery technology because they can provide long service times and stable performance.
Lead-acid battery application
- Automobiles and motorcycles: Traditional internal combustion engine vehicles and motorcycles often use lead-acid batteries as starting batteries because of their lower cost and reliability.
- UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) : Lead-acid batteries are widely used in UPS systems to provide temporary power backup to ensure that equipment continues to operate in the event of a power outage or grid failure.
- Solar energy storage systems: In some low-cost and small solar systems, lead-acid batteries are also used to store solar power for subsequent use.
In short, lithium batteries have a wide range of applications in mobile devices, electric vehicles and household electronics and other fields, due to its high energy density and long life, suitable for scenarios with high performance and volume weight requirements.
In contrast, lead-acid batteries are mainly used in traditional vehicle starter batteries, UPS systems and some small solar energy storage systems, suitable for cost-sensitive applications and scenarios with low energy density requirements.
Conclusion
As with any large purchase, such as solar and batteries (paired or alone), you need to consider your options. You can contact GYCX Solar to get a turnkey quote for your solar installation from a pre-screened local solar installer. If you’re interested in pairing battery storage with your system, you can click here to get a quote now. Even if solar installers don’t install batteries themselves, they can design solar panel systems so that you can add batteries later.
